[ad_1]
News briefs for the week check out Ziggy, a cellular EV charging robotic, for all these instances when stationary charging is inconvenient; then a large robotic that climbs large wind generators by copying the way in which a Koala climbs timber, then to Taiwan the place a UGV scours sewers searching for mosquito breeding grounds, then to a different astounding first for ChatGPT: constructing a robotic; and eventually, a light-weight 3-lbs., exosuit to tackle all types of chores, even when solely to scale back drained legs on the workplace or climbing mountain trails.
Mobile EV charging robots
Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations are proliferating by the tens of 1000’s as a way to accommodate the anticipated thousands and thousands of  EVs (40% of complete passenger automobile gross sales) anticipated by 2030. For essentially the most half, EV charging stations are stationary. Drivers have to again right into a station, get out and manually insert the charging plug.
EVs (40% of complete passenger automobile gross sales) anticipated by 2030. For essentially the most half, EV charging stations are stationary. Drivers have to again right into a station, get out and manually insert the charging plug.
For many, such an EV charging expertise will be troublesome, harmful, and even unimaginable. In specific, these with everlasting or short-term bodily disabilities, pregnant ladies, and the aged are susceptible to have issues recharging. Then too, there’s the infuriating expertise of underdeveloped EV infrastructure the place there’s by no means an accessible charger.
Enter Ziggy, a robotic, cellular EV charging station “that’s designed to live in parking areas, where drivers can summon it through an app to come charge their vehicle,” says Car & Driver.
Startup, LA-based EV Safe Charge, started improvement of Ziggy in 2019, with the cellular models scheduled for delivery in late 2023.
“Roughly the size of a refrigerator, Ziggy is a battery on wheels that will be able to autonomously navigate parking areas to reserve drivers’ spots and charge their cars. And of course, it’s got ads on it.”
Koalas, robots, and wind farms
How about nature-inspiring know-how? Northern Spain’s Navarre-based KoalaLifter has developed a large robotic crane that mimics the way in which a koala climbs a tree. The koala’s distinctive strategy of wrapping its limbs round a tree after which hoisting itself up is  used to maneuver the appropriately named KoalaLifter up into wind generators to both construct, exchange components or restore the large buildings.
used to maneuver the appropriately named KoalaLifter up into wind generators to both construct, exchange components or restore the large buildings.
Every yr, greater than 18 000 new wind generators are put in and round 20 000 upkeep operations are carried out. The EU-funded KoalaLifter, with its autonomous, self-climbing functionality, is “virtually independent of tower height, weight to be lifted, and wind speed limits.”
“KoalaLifter System,” says the corporate, “is a disruptive lifting device that uses friction collars to embrace the Wind Turbine Generator (WTG) tower to make possible an autonomous, self-climbing capability, eliminating the need for high-tonnage cranes.”
The system operates with out employees near the hundreds, is transported by truck, and wishes just one operator to place the system for its climb.
Taiwan’s mosquito-hunting UGV
Led by Wei-Liang Liu, an investigator with Taiwan’s National Mosquito-Borne Diseases Control Research Center, researchers designed an unmanned floor automobile (UGV) to scour cracks and crevices deep within the sewers of Kaohsiung City, a significant metropolis (1.7 million) within the 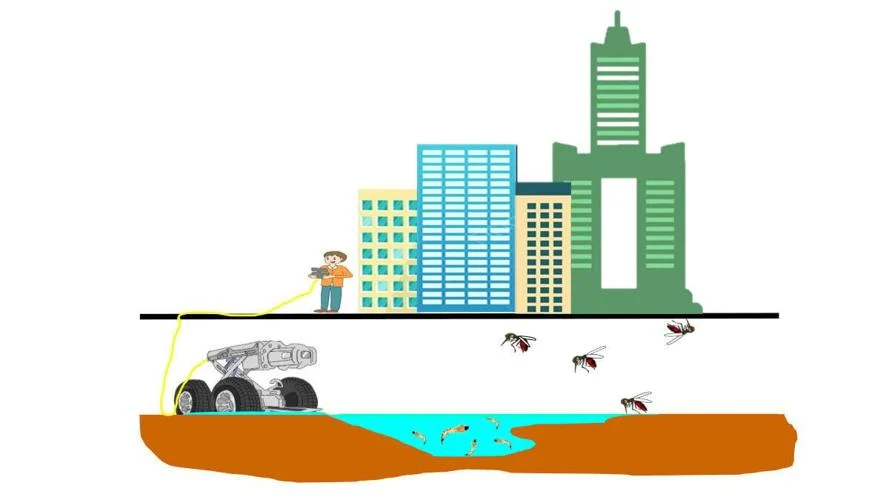 south of Taiwan.
south of Taiwan.
Dengue fever, yellow fever, and the Zika virus lurk underground, are born to a number of mosquito species there, after which come up into Kaohsiung City to transmit viruses to the overall inhabitants.
To eradicate the underground breeding areas would, say authorities, put an enormous crimp within the metropolis’s mosquito inhabitants and the dengue virus devastation that afflicts the town.
The UGV has confirmed to be a extremely efficient mosquito hunter.
“Researchers combined a crawling robot, wire-controlled cable car and real-time monitoring system into an unmanned ground vehicle system (UGV) that can take high-resolution, real-time images of areas within sewers.”
The system is yearly deployed from May to August in 5 administrative districts in Kaohsiung City, specific emphasis is given to lined roadside sewer ditches.
And it labored! The UGV robotic hunter helped dramatically drop the town’s mosquito inhabitants by practically 70 %.
A double first-ever for ChatGPT and robots
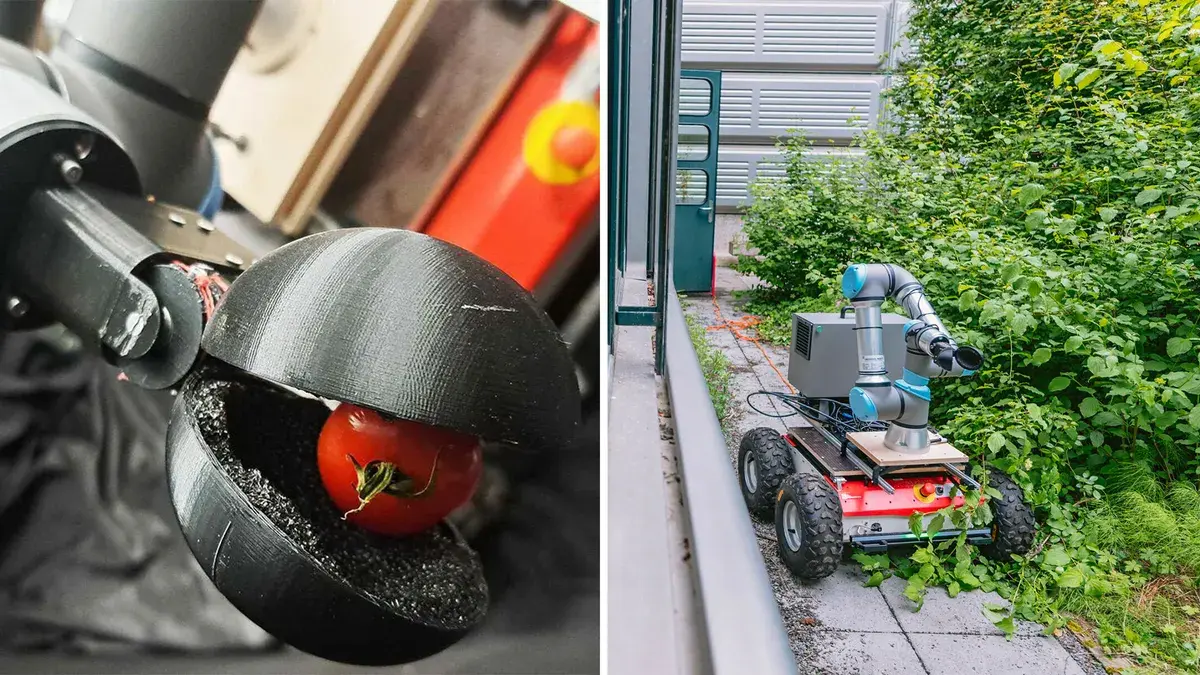
ChatGPT not solely designed a crop-picking robotic, but in addition specified for which crop it ought to be constructed!
Researchers at EPFL (Swiss technical college) and TU Delft (Netherlands) have collaborated with ChatGPT-3 to design a robotic, which turned out to be a cellular harvesting robotic with an arm for tomato choosing.
 It’s attending to be that ChatGPT, and generative AI basically, know no bounds as to being influencers of different industries and know-how. And just lately it was given an opportunity to impression the design of robots.
It’s attending to be that ChatGPT, and generative AI basically, know no bounds as to being influencers of different industries and know-how. And just lately it was given an opportunity to impression the design of robots.
A gaggle of roboticists picked agriculture and ChatGPT prompt tomato choosing due to its excessive financial worth. “We needed ChatGPT to design not only a robotic, however one that’s really helpful,” stated Cosimo Della Santina, assistant professor, and Ph.D. pupil Francesco Stella, each from TU Delft (Netherlands).
With a international tomato market of $200 billion yearly, it appears to be like very very like ChatGPT picked nicely.
This might get fascinating. Nature Machine Intelligence is out with an article the place the roboticists state: “We show that large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, can guide the robot design process, on both the conceptual and technical level, and we propose new human–AI co-design strategies and their societal implications.”
That’s an absolute bombshell!
For occasion, might ChatGPT reconceptualize and redesign cobot welding or robotic palletizing? Looks like we’ll quickly see.
For now, ChatGPT has shocked nearly everybody by designing an agricultural robotic…and to everybody’s amazement, it specified which crop for it to choose.
The researchers, intent on using ChatGPT for his or her design and construct, additionally needed to discover the various levels of cooperation between people and Large Language Models (LLM), of which ChatGPT is one.
And as an additional bonus, ChatGPT prompt a new-age gripper comprised of silicone or rubber to keep away from crushing tomatoes.
Okay, now let’s see how nicely it sells. Maybe ChatGPT is aware of.
Off-the-rack, ready-to-wear robots!
As the evolution of exoskeletons (additionally known as wearable robots) progresses, the {hardware} retains cutting down whereas the number of potential use instances continues to rise.
The cumbersome, heavy-duty body for supporting paralysis sufferers is pointless for office assistant gear like that used for unloading vehicles or pallets filled with heavy instances and in addition as coaching outfits that allow athletes to extend energy and endurance.
 Evermore light-weight exosuits are actually speeding into {the marketplace} to tackle all types of chores, even when solely to scale back drained legs on the workplace or climbing mountain trails.
Evermore light-weight exosuits are actually speeding into {the marketplace} to tackle all types of chores, even when solely to scale back drained legs on the workplace or climbing mountain trails.
One such beginner is Korea’s WIRobotics (based in 2021) which is out with a one-size-fits-all “ultralight, walking aid, wearable robot” named WIM.
“While wearable robots so far have been mainly used in the workplace, WIM is expected to become a wearable robot for everyday life for the general public,” introduced the brand new robotic maker.
Co-CEO Lee Yeon-baek stated, “WIM would be the first product of such wearable mobility, though weight, measurement, portability and utilization time have been challenges to beat to ensure that present wearable robots to enter the dwelling and dealing areas of abnormal individuals.”
WIM, says the corporate’s web site, “weighs only 1.4 kg (3 lbs.) and has a compact size, so it is easy to carry and can be attached and detached within 30 seconds. While wearing it, it is possible not only to perform various tasks such as driving, but also to sit or lie down to take a break.”
The firm’s different co-CEO Kim Yong-jae added: “WIM not only collects the wearer’s posture and motion information, but also analyzes the wearer’s strength and balance information, and selects a mode based on the data to selectively change walking posture, efficiency, and strength.”
![]()
