[ad_1]
Caching is a ubiquitous thought in pc science that considerably improves the efficiency of storage and retrieval methods by storing a subset of widespread gadgets nearer to the shopper primarily based on request patterns. An vital algorithmic piece of cache administration is the choice coverage used for dynamically updating the set of things being saved, which has been extensively optimized over a number of many years, leading to a number of efficient and sturdy heuristics. While making use of machine studying to cache insurance policies has proven promising outcomes lately (e.g., LRB, LHD, storage purposes), it stays a problem to outperform sturdy heuristics in a means that may generalize reliably past benchmarks to manufacturing settings, whereas sustaining aggressive compute and reminiscence overheads.
In “HALP: Heuristic Aided Learned Preference Eviction Policy for YouTube Content Delivery Network”, introduced at NSDI 2023, we introduce a scalable state-of-the-art cache eviction framework that’s primarily based on discovered rewards and makes use of preference studying with automated suggestions. The Heuristic Aided Learned Preference (HALP) framework is a meta-algorithm that makes use of randomization to merge a light-weight heuristic baseline eviction rule with a discovered reward mannequin. The reward mannequin is a light-weight neural community that’s repeatedly educated with ongoing automated suggestions on choice comparisons designed to imitate the offline oracle. We focus on how HALP has improved infrastructure effectivity and consumer video playback latency for YouTube’s content material supply community.
Learned preferences for cache eviction selections
The HALP framework computes cache eviction selections primarily based on two elements: (1) a neural reward mannequin educated with automated suggestions through choice studying, and (2) a meta-algorithm that mixes a discovered reward mannequin with a quick heuristic. As the cache observes incoming requests, HALP repeatedly trains a small neural community that predicts a scalar reward for every merchandise by formulating this as a choice studying methodology through pairwise choice suggestions. This side of HALP is much like reinforcement studying from human suggestions (RLHF) methods, however with two vital distinctions:
- Feedback is automated and leverages well-known outcomes in regards to the construction of offline optimum cache eviction insurance policies.
- The mannequin is discovered repeatedly utilizing a transient buffer of coaching examples constructed from the automated suggestions course of.
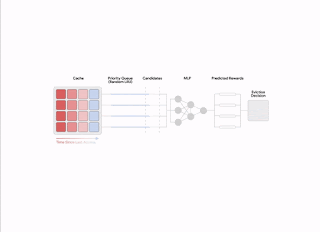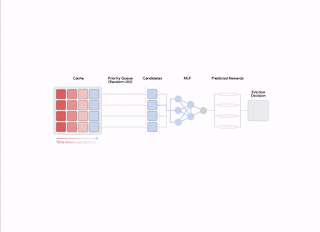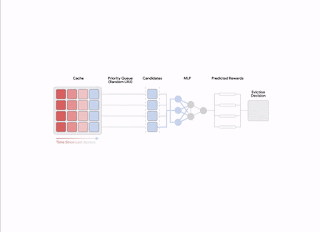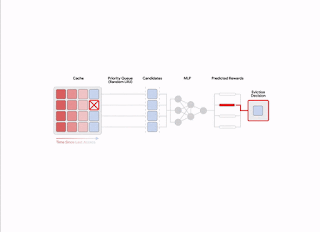
The eviction selections depend on a filtering mechanism with two steps. First, a small subset of candidates is chosen utilizing a heuristic that’s environment friendly, however suboptimal by way of efficiency. Then, a re-ranking step optimizes from inside the baseline candidates through the sparing use of a neural community scoring perform to “boost” the standard of the ultimate determination.
As a manufacturing prepared cache coverage implementation, HALP not solely makes eviction selections, but in addition subsumes the end-to-end means of sampling pairwise choice queries used to effectively assemble related suggestions and replace the mannequin to energy eviction selections.
A neural reward mannequin
HALP makes use of a lightweight two-layer multilayer perceptron (MLP) as its reward mannequin to selectively rating particular person gadgets within the cache. The options are constructed and managed as a metadata-only “ghost cache” (much like classical insurance policies like ARC). After any given lookup request, along with common cache operations, HALP conducts the book-keeping (e.g., monitoring and updating characteristic metadata in a capacity-constrained key-value retailer) wanted to replace the dynamic inside illustration. This contains: (1) externally tagged options offered by the consumer as enter, together with a cache lookup request, and (2) internally constructed dynamic options (e.g., time since final entry, common time between accesses) constructed from lookup occasions noticed on every merchandise.
HALP learns its reward mannequin absolutely on-line ranging from a random weight initialization. This would possibly look like a foul thought, particularly if the selections are made solely for optimizing the reward mannequin. However, the eviction selections depend on each the discovered reward mannequin and a suboptimal however easy and sturdy heuristic like LRU. This permits for optimum efficiency when the reward mannequin has absolutely generalized, whereas remaining sturdy to a briefly uninformative reward mannequin that’s but to generalize, or within the means of catching as much as a altering surroundings.
Another benefit of on-line coaching is specialization. Each cache server runs in a probably totally different surroundings (e.g., geographic location), which influences native community circumstances and what content material is domestically widespread, amongst different issues. Online coaching mechanically captures this data whereas decreasing the burden of generalization, versus a single offline coaching answer.
Scoring samples from a randomized precedence queue
It will be impractical to optimize for the standard of eviction selections with an solely discovered goal for 2 causes.
- Compute effectivity constraints: Inference with a discovered community will be considerably costlier than the computations carried out in sensible cache insurance policies working at scale. This limits not solely the expressivity of the community and options, but in addition how typically these are invoked throughout every eviction determination.
- Robustness for generalizing out-of-distribution: HALP is deployed in a setup that entails continuous studying, the place a shortly altering workload would possibly generate request patterns that is likely to be briefly out-of-distribution with respect to beforehand seen knowledge.
To handle these points, HALP first applies a reasonable heuristic scoring rule that corresponds to an eviction precedence to determine a small candidate pattern. This course of is predicated on environment friendly random sampling that approximates precise precedence queues. The precedence perform for producing candidate samples is meant to be fast to compute utilizing current manually-tuned algorithms, e.g., LRU. However, that is configurable to approximate different cache alternative heuristics by enhancing a easy price perform. Unlike prior work, the place the randomization was used to tradeoff approximation for effectivity, HALP additionally depends on the inherent randomization within the sampled candidates throughout time steps for offering the required exploratory variety within the sampled candidates for each coaching and inference.
The remaining evicted merchandise is chosen from among the many equipped candidates, equal to the best-of-n reranked pattern, akin to maximizing the anticipated choice rating in accordance with the neural reward mannequin. The identical pool of candidates used for eviction selections can also be used to assemble the pairwise choice queries for automated suggestions, which helps decrease the coaching and inference skew between samples.
 |
| An overview of the two-stage course of invoked for every eviction determination. |
Online choice studying with automated suggestions
The reward mannequin is discovered utilizing on-line suggestions, which is predicated on mechanically assigned choice labels that point out, wherever possible, the ranked choice ordering for the time taken to obtain future re-accesses, ranging from a given snapshot in time amongst every queried pattern of things. This is much like the oracle optimum coverage, which, at any given time, evicts an merchandise with the farthest future entry from all of the gadgets within the cache.
 |
| Generation of the automated suggestions for studying the reward mannequin. |
To make this suggestions course of informative, HALP constructs pairwise choice queries which can be almost certainly to be related for eviction selections. In sync with the standard cache operations, HALP points a small variety of pairwise choice queries whereas making every eviction determination, and appends them to a set of pending comparisons. The labels for these pending comparisons can solely be resolved at a random future time. To function on-line, HALP additionally performs some further book-keeping after every lookup request to course of any pending comparisons that may be labeled incrementally after the present request. HALP indexes the pending comparability buffer with every ingredient concerned within the comparability, and recycles the reminiscence consumed by stale comparisons (neither of which can ever get a re-access) to make sure that the reminiscence overhead related to suggestions technology stays bounded over time.
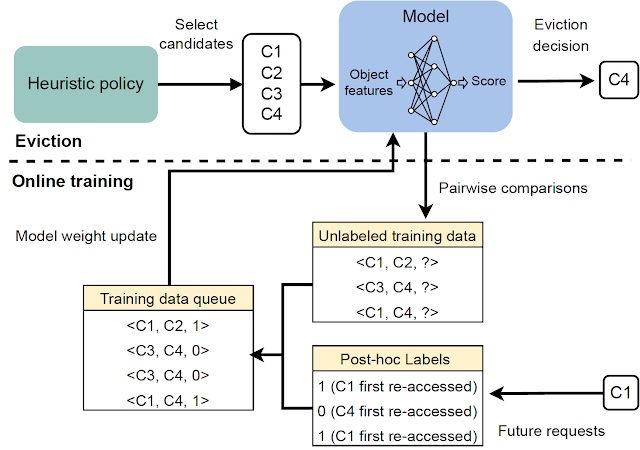 |
| Overview of all most important elements in HALP. |
Results: Impact on the YouTube CDN
Through empirical evaluation, we present that HALP compares favorably to state-of-the-art cache insurance policies on public benchmark traces by way of cache miss charges. However, whereas public benchmarks are a great tool, they’re hardly ever adequate to seize all of the utilization patterns internationally over time, to not point out the various {hardware} configurations that we have now already deployed.
Until just lately, YouTube servers used an optimized LRU-variant for reminiscence cache eviction. HALP will increase YouTube’s reminiscence egress/ingress — the ratio of the entire bandwidth egress served by the CDN to that consumed for retrieval (ingress) resulting from cache misses — by roughly 12% and reminiscence hit charge by 6%. This reduces latency for customers, since reminiscence reads are quicker than disk reads, and in addition improves egressing capability for disk-bounded machines by shielding the disks from visitors.
The determine beneath reveals a visually compelling discount within the byte miss ratio within the days following HALP’s remaining rollout on the YouTube CDN, which is now serving considerably extra content material from inside the cache with decrease latency to the top consumer, and with out having to resort to costlier retrieval that will increase the working prices.
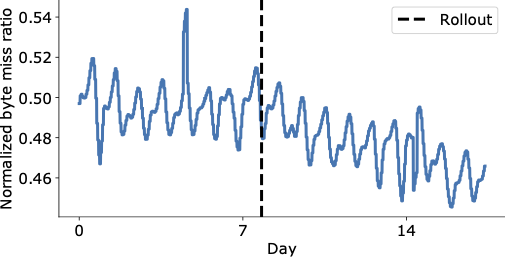 |
| Aggregate worldwide YouTube byte miss ratio earlier than and after rollout (vertical dashed line). |
An aggregated efficiency enchancment might nonetheless conceal vital regressions. In addition to measuring general influence, we additionally conduct an evaluation within the paper to grasp its influence on totally different racks utilizing a machine stage evaluation, and discover it to be overwhelmingly optimistic.
Conclusion
We launched a scalable state-of-the-art cache eviction framework that’s primarily based on discovered rewards and makes use of preference studying with automated suggestions. Because of its design selections, HALP will be deployed in a fashion much like another cache coverage with out the operational overhead of getting to individually handle the labeled examples, coaching process and the mannequin variations as further offline pipelines frequent to most machine studying methods. Therefore, it incurs solely a small further overhead in comparison with different classical algorithms, however has the additional benefit of having the ability to benefit from further options to make its eviction selections and repeatedly adapt to altering entry patterns.
This is the primary large-scale deployment of a discovered cache coverage to a extensively used and closely trafficked CDN, and has considerably improved the CDN infrastructure effectivity whereas additionally delivering a greater high quality of expertise to customers.
Acknowledgements
Ramki Gummadi is now a part of Google DeepMind. We wish to thank John Guilyard for assist with the illustrations and Richard Schooler for suggestions on this submit.
