[ad_1]

By Sabrina Corlette, Rachel Swindle, and Rachel Schwab
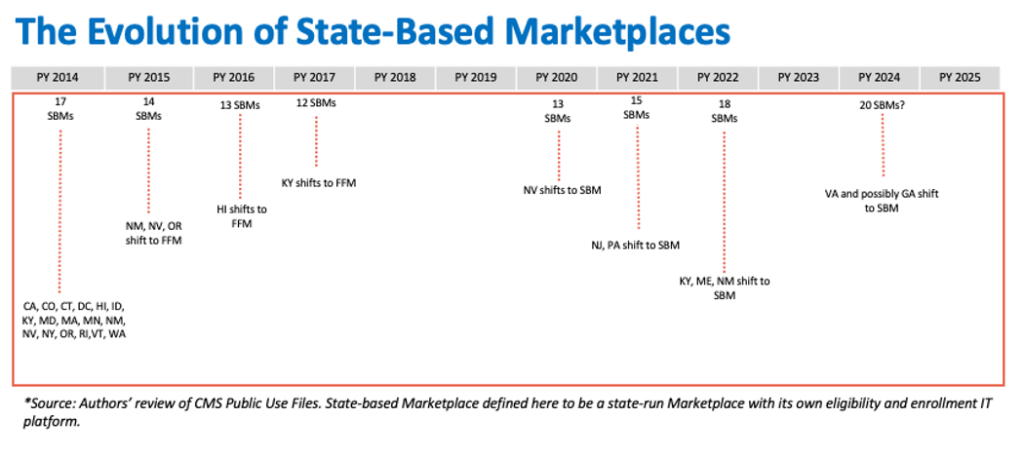
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) established medical insurance Marketplaces (or “Exchanges”) to facilitate enrollment in complete and inexpensive medical insurance plans. The ACA envisioned that the Marketplaces can be primarily state-run, with the federal authorities stepping in as a backstop. In observe, due partly to deep anti-ACA sentiment amongst some state policymakers, when the Marketplaces launched in 2013, solely 17 states and the District of Columbia had been state-run Marketplaces with their very own IT eligibility and enrollment platforms. The federal authorities needed to run the Marketplaces within the remaining 33 states, and because the inaugural yr, some state-run Marketplaces have used the federal enrollment platform HealthCare.gov. Over the course of the primary decade of the ACA’s Marketplaces, the variety of state-based Marketplaces (SBM) has fluctuated from 17 within the first yr, to a low of 12 in plan yr 2017, to the present 18 in 2023. (See Exhibit). States transitioning to a full SBM lately sought management partly as a result of the Trump administration’s efforts to roll again the ACA led to instability of their insurance coverage markets and a rise within the numbers of uninsured. The capacity to adapt an SBM to state circumstances and priorities has enabled these states to construct on the ACA and broaden enrollment.
More not too long ago, a number of further states have indicated they could undertake a transition to an SBM, together with Georgia and Texas, the place opposition to the ACA stays a bedrock precept for a lot of lawmakers. With general Marketplace enrollment at an all-time excessive, and tens of millions extra individuals poised to transition from Medicaid to industrial insurance coverage, the position of the ACA’s Marketplaces as a well being protection security web has by no means been extra pivotal. Yet federal guidelines implementing the ACA impose few requirements for launching and sustaining a Marketplace that adequately serves customers and builds on enrollment good points. Given states’ curiosity in taking up operation of the Marketplaces, it could be time for the federal authorities to ascertain a stronger federal ground.
The Need For Minimum Standards Before Operating a State-based Marketplace
To date, SBMs have been main the way in which in the direction of better insurance coverage protection and an improved shopper expertise. They are investing closely in advertising, outreach, and enrollment help, coordinating with Medicaid companies to scale back churn, elevating the bar on high quality for collaborating insurers, and performing to enhance the patron buying expertise. Many SBMs have applied revolutionary methods to succeed in the remaining uninsured, resembling state-funded subsidies, protection for undocumented residents, and “easy” or automated enrollment.
In the final two years, the federally facilitated Marketplace (FFM) has been catching up. The FFM has dramatically elevated funding for advertising and enrollment help. Federal officers have additionally applied new insurance policies to lengthen enrollment home windows, simplify plan decisions, broaden eligibility for tax credit (by fixing the “family glitch”), and cut back the quantity of paperwork for customers to take away enrollment obstacles. These efforts are paying off, with record-breaking FFM enrollment in 2023.
Any state in search of to transition from HealthCare.gov to SBM standing at the moment thus has the next danger of backsliding on these protection good points. The ACA specified that state Marketplaces predating legislation’s enactment, resembling Massachusetts’s Marketplace, had been presumed to qualify beneath the brand new federal requirements for SBMs provided that they continued to cowl roughly the identical portion of the inhabitants projected to be lined nationally beneath the ACA. The assumption was that SBMs must construct on, not detract from, the ACA’s protection objectives.
Yet not all state leaders in search of to launch an SBM share a dedication to common insurance coverage protection. Indeed, 10 states, together with Georgia and Texas, haven’t taken up the choice to broaden Medicaid protection to their poorest residents. And though states are typically the primary line of enforcement of the ACA’s market reforms, Texas has declined to play this position, and as an alternative depends on federal enforcement. Moreover, Georgia has previously sought permission to bypass a number of key Marketplace necessities, together with the centralized enrollment web site. Instead, the state proposed to ship customers to non-public insurers and brokers, each of which have monetary incentives to restrict significant plan comparability.
Marketplace Roles and Responsibilities
Under present federal guidelines, SBMs have a protracted listing of vital tasks, however are topic to comparatively minimal federal requirements for the way they carry out these duties.
Governance
States can set up a Marketplace as a governmental company or non-profit entity. Marketplaces run by impartial state companies and non-profit entities should have a governing board sure by a proper and public constitution or by-laws, maintain common and open conferences introduced upfront, and meet sure membership requirements, resembling a ceiling on members with ties to the medical insurance trade. Marketplace boards should even have publicly out there insurance policies governing conflicts of curiosity and monetary curiosity disclosures, ethics rules, and accountability and transparency requirements. Federal guidelines implementing the ACA don’t specify the variety of instances Marketplace boards should meet yearly, how far upfront conferences should be introduced, the variety of people on the governing board, if there are time period limits for voting board members, or how board members are chosen or appointed.
Funding
In establishing a Marketplace, states should guarantee it’s financially self-sufficient. States have broad flexibility to decide on the mechanism by which they fund their Marketplace, resembling an evaluation or price on insurers or a state appropriation of different funds. States can also apply for future federal grants, resembling when Congress allocated further funding beneath the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA).
Stakeholder Consultation
The ACA requires Marketplaces to seek the advice of with stakeholders on a “regular and ongoing basis,” together with Marketplace enrollees, people and entities facilitating Marketplace enrollments, small companies representatives, the state’s Medicaid company, “advocates for enrolling hard to reach populations,” federally acknowledged Tribes, public well being consultants, suppliers, massive employers, insurers, and brokers/brokers. Federal guidelines don’t specify the frequency or kind for stakeholder session, which parts of the Marketplace operations are topic to stakeholder enter, or a course of to make sure stakeholder suggestions is integrated into Marketplace insurance policies and practices.
More Than a Website
The Marketplaces should carry out a number of features designed to make sure that customers are in a position to perceive their choices, decide their eligibility for premium tax credit, and enroll in a well being plan that meets minimal requirements. These features embrace:
Plan Management. States that function their very own Marketplaces are liable for certifying that well being plans are “qualified health plans” (QHPs), merchandise eligible to be bought on the Marketplace. This means the plans should meet federal and state profit necessities, premium ranking guidelines, prescribed “actuarial value” or plan generosity ranges, prohibitions towards discriminatory profit design or pre-existing situation limitations, and community adequacy, amongst different requirements. While some necessities apply to plans in each Marketplace, others, resembling particular community adequacy requirements, differ relying on whether or not the Marketplace is state- or federally run. Some Marketplaces that function independently of their state division of insurance coverage (DOI) nonetheless depend on their DOI for sure plan administration duties.
Online Eligibility and Enrollment Platform. Marketplaces should keep a web site for customers to buy and enroll in protection in a approach that’s accessible for these with disabilities and/or restricted English language proficiency. Websites should present, for instance, standardized details about QHPs to facilitate plan comparability, together with premium and cost-sharing particulars, a shopper price calculator, a abstract of advantages and protection for every product out there, high quality rankings, and supplier directories. Marketplace web sites additionally function an entry level for different insurance coverage affordability applications, resembling Medicaid, both by operating a full eligibility willpower or directing customers to the suitable state company. The nature of medical insurance enrollment additionally requires Marketplaces to gather delicate private info, and accordingly Marketplaces should meet federal privateness requirements or face financial penalties.
Many of the primary Marketplace web sites had been a catastrophe, main a number of to pivot to the FFM of their first yr. Since then, each federal and state platforms have improved significantly and efficiently enrolled tens of millions of customers. However, the continued upkeep and operation of those web sites requires a substantial funding. Federal coverage modifications, such because the latest premium subsidy enhancements in ARPA and the Biden administration’s “family glitch” repair, can even require speedy and costly updates to on-line eligibility programs. In each of these situations, some SBMs weren’t in a position to make the required modifications to their web sites in a well timed trend.
Marketplace Call Centers. SBMs are required to function a toll-free name middle to subject questions and requests from customers concerning the eligibility and enrollment course of. Other than the requirement to have a toll-free name middle, federal guidelines don’t impose exacting requirements on Marketplaces, resembling staffing ranges or most name wait instances. Some Marketplace name facilities have skilled system outages and significant wait instances throughout their annual enrollment intervals. Updated, clear federal requirements and ongoing oversight of customer support high quality might assist keep away from comparable points sooner or later.
Outreach and Enrollment Assistance. Federal rules require SBMs to “conduct outreach and education activities . . . to educate consumers about the [Marketplace] and insurance affordability programs to encourage participation.” Other than being accessible for individuals with restricted English proficiency and other people with disabilities, SBMs have important flexibility in how and to what extent they conduct this outreach.
SBMs are required to run and fund their very own Navigator applications, though federal guidelines depart a lot of the particulars of these applications to the states. For occasion, though all Marketplaces should set up sure coaching requirements (resembling coaching on assembly the wants of underserved populations), states can decide the content material and frequency of these trainings.
Federal guidelines additionally don’t set up a minimal funding degree required for both Navigator applications or outreach campaigns. As a outcome, there’s a wide selection of SBM funding ranges in these confirmed ways for rising protection.
Process for Transitioning to a State-Based Marketplace
The course of for transitioning to an SBM typically requires the state to submit two fundamental parts to the federal authorities: (1) a letter declaring the intent to transition, and (2) an “Exchange Blueprint” to reveal the state’s capacity to function a Marketplace. Federal regulators have made some changes to the Blueprint over time, most notably permitting states to easily attest that they meet most of the federal necessities to function a Marketplace as an alternative of submitting documentation offering proof of compliance. And, regardless of stakeholder concern, starting in 2024 Blueprint approval is now not required not less than 14 months previous to the beginning of the brand new SBM’s preliminary open interval, permitting for a shorter timeframe between federal approval and an SBM changing into operational to serve customers.
Setting a Bar: Potential Minimum Standards
Without further minimal requirements for the design and operation of an SBM, there’s a danger that the patron expertise with the Marketplace will worsen, making enrollment more difficult and in the end lowering protection charges. While the ACA clearly envisions a excessive diploma of state autonomy over the operation of the Marketplaces, a couple of further requirements for SBMs might embrace, for instance:
- A deliberative SBM transition course of. Hiring employees with the required abilities and experience, procuring the required IT and different service suppliers, testing programs, constructing model consciousness, and interesting with assisters, carriers, and different stakeholders all take time. Given the stakes for customers, it’s not a course of that ought to be rushed. It is also useful for states to spend a minimal of 1 yr as an SBM on the federal platform (SBM-FP) earlier than totally transitioning to an SBM. This would offer a while for CMS to evaluate the state’s strategy to governance, shopper outreach and help, and stakeholder engagement, earlier than handing over full management.
- Transparency and neighborhood engagement. States ought to be soliciting and incorporating public touch upon their proposed Blueprint, and publicly posting their Blueprint functions. Greater transparency surrounding SBMs’ income supply(s) and spending, resembling extra distinguished public posting of audits, in addition to knowledge on key metrics resembling plan alternatives, effectuated enrollments, name middle wait instances, and spending on Navigators and shopper help can also be vital.
- An funding in shopper outreach and help. Given the confirmed effectiveness of shopper outreach and help, will probably be essential for SBMs to fulfill minimal efficiency requirements for shopper outreach, name middle assist, and Navigator applications.
- Standards for Marketplace well being plans. Enrollees in all Marketplaces need to have plans that meet minimal standards for certification. Although CMS has thus far avoided extending some requirements, resembling community adequacy, to insurers in SBM states, a federal ground might be useful to keep away from a large divergence in shopper protections throughout states. At a minimal, if a state is just not imposing the ACA market reforms, it shouldn’t be working an SBM.
Looking Ahead
To date, states have chosen to function their very own Marketplace based mostly on a dedication to inexpensive, complete medical insurance for all their residents, with the SBM serving as a vital device for reaching that objective. But in some states which will search SBM standing sooner or later, notably people who have demonstrated antagonism in the direction of the ACA’s protection expansions and shopper protections, additional federal guardrails might assist cut back the danger of a decline in customers’ expertise and, within the worst-case state of affairs, a reversal of the latest good points in insurance coverage protection.
The authors thank Justin Giovannelli, Jason Levitis, Sarah Lueck, Claire Heyison and Tara Straw for his or her considerate evaluation and enhancing of this submit.
[ad_2]
