[ad_1]
Microsoft has shared steering to assist organizations verify if hackers focused or compromised machines with the BlackLotus UEFI bootkit by exploiting the CVE-2022-21894 vulnerability.
Organizations and people also can use Microsoft’s recommendation to get well from an assault and to forestall menace actors utilizing BlackLotus from attaining persistence and evading detection.
BlackLotus has been obtainable since final yr on hacking boards, marketed as a chunk of malware that evades antivirus detection, resists elimination makes an attempt, and may disable numerous security measures (e.g. Defender, HVCI, BitLocker). The worth for a license was $5,000, with rebuilds obtainable for $200.
The capabilities of the malware had been confirmed in early March by researchers at ESET cybersecurity firm, who famous that the malware functioned precisely as marketed.
Locating BlackLotus an infection clues
Malware for the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is especially difficult to detect as these threats run earlier than the working system, being succesful to deploy payloads early on within the boot course of to disable safety mechanisms.
Malware for the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is especially difficult to detect as any such menace runs earlier than the working system begins, permitting it to deploy payloads early within the boot course of to disable safety mechanisms.
Analyzing units compromised with BlackLotus, the Microsoft Incident Response group recognized a number of factors within the malware set up and execution course of that permit its detection.
The researchers word that defenders can search for the next artifacts to find out a BlackLotus UEFI bootkit an infection:
- Recently created and locked bootloader recordsdata
- Presence of a staging listing used in the course of the BlackLotus set up within the EPS:/ filesystem
- Registry key modification for the Hypervisor-protected Code Integrity (HVCI)
- Network logs
- Boot configuration logs
Boot partition artifacts
Since BlackLotus wants to jot down malicious bootloader recordsdata to the EFI system partition, additionally known as ESP, it’s going to lock them to forestall their deletion or modification.
Recently modified and locked recordsdata within the ESP location, particularly in the event that they match recognized BlackLotus bootloader file names “should be considered highly suspect.” It is suggested to take away the units from the community and study them for proof of exercise associated to BlackLotus.
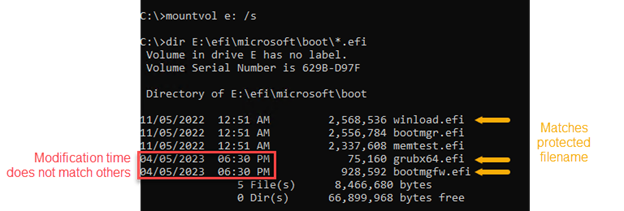
Microsoft recommends utilizing the mountvol command-line utility to mount the boot partition and verify the creation date of the recordsdata with mismatched creation occasions.
supply: Microsoft
You can mount the ESP partition utilizing the next command in a Command Prompt with Administrator privileges:
mountvol[available drive letter] /sFor occasion, if the G: drive letter is free, you possibly can execute this command:
mountvol g: /sIf the modification time doesn’t look suspicious, menace hunters can attempt to calculate the hash of the bootloader file. On a compromised gadget the output ought to be a file entry error as a result of BlackLotus locks them to forestall their tampering.
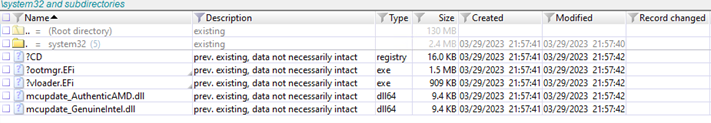
Another inform of BlackLotus is the presence of the “/system32/” listing on the ESP, which is the storage location for the recordsdata required to put in the UEFI malware.
Microsoft says that profitable set up of BlackLotus ends in deleting the recordsdata inside “ESP:/system32/” however the listing stays. Forensic analysts can use this to seek for the eliminated recordsdata.
supply: Microsoft
Registry, logs, and community clues
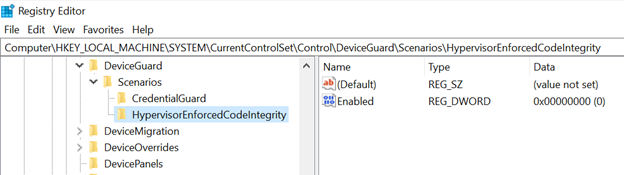
One of the BlackLotus capabilities is to disable the hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI), which permits it to load unsigned kernel code.
This is achieved by altering to 0 (zero) the Enabled worth of the HVCI registry key, as within the picture beneath.
supply: Microsoft
A second security characteristic that BlackLotus disables is Microsoft Defender Antivirus, the default safety agent on the Windows working system.
This motion might go away traces within the Windows Event Logs within the type of an entry beneath the Microsoft-Windows-Windows Defender/Operational Log.
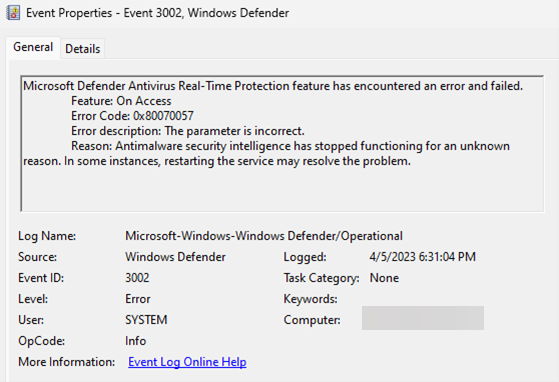
supply: Microsoft
Turning off Defender may generate an Event ID 7023 within the System occasion log because of the service stopping unexpectedly.
Microsoft investigators advise menace hunters to look at community logs for outbound connections from winlogon.exe on port 80, which can be indicative of BlackLotus attempting to speak with its command and management (C2) server.
“This is the result of the injected HTTP downloader function of BlackLotus connecting to the C2 server or performing network configuration discovery” – Microsoft
Additional proof of BlackLotus compromise could be current within the boot configuration logs – MeasuredBoot logs, that present particulars in regards to the Windows boot course of.
When the bootkit turns into lively, two boot drivers develop into obtainable, particularly grubx64.efi and winload.efi. By evaluating the logs for every reboot of the system, analysts can discover the parts which have been added or faraway from every machine boot.
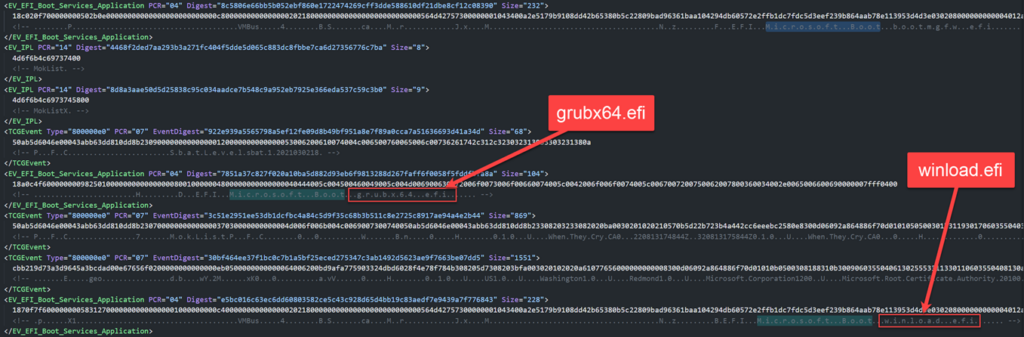
supply: Microsoft
Microsoft warns that accessing the MeasuredBoot log recordsdata is feasible utilizing a forensic picture or uncooked NTFS studying instrument.
The knowledge could be learn after decoding and changing it to XML or JSON file format. Microsoft gives a pattern script based mostly on the open-source TCGLogTools for parsing and extracting the logs
Below is an instance of the BlackLotus drivers the pattern script confirmed on an contaminated machine:
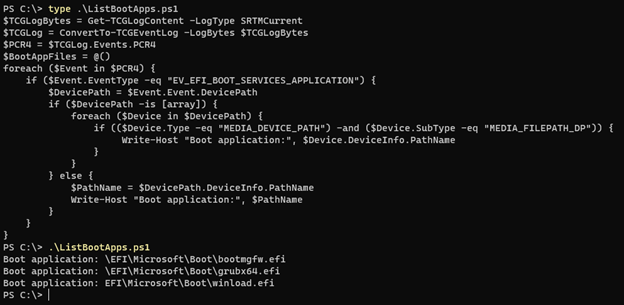
supply: Microsoft
Preventing BlackLotus compromise
Cleaning a machine after a BlackLotus an infection requires eradicating it from the community and reinstalling it with a clear working system and EFI partition, or restoring from a clear backup with an EFI partition.
While the post-infection artifacts are revealing in figuring out the kind of malware used, defenders can stop the compromise by detecting an intrusion earlier than the adversary can deploy UEFI malware.
Launching a UEFI bootkit, although, requires privileged entry to the goal machine, both distant or bodily, which means {that a} first-stage menace and an preliminary entry vector precede the persistent an infection.
To fend off an an infection by way of BlackLotus or different malware exploiting CVE-2022-21894, Microsoft recommends organizations apply the precept of least privilege and credential hygiene.
“Avoid the use of domain-wide, admin-level service accounts. Restricting local administrative privileges can help limit installation of remote access trojans (RATs) and other unwanted applications” – Microsoft
By implementing a number of layers of safety controls, the so-called protection in-depth methods, organizations can cut back the danger of an adversary gaining entry or administrative privilege within the atmosphere.
This can primarily cease a BlackLotus assault in its earlier phases earlier than the menace actor can compromise a person or service account credentials to maneuver laterally on the community and escalate their privileges.
