[ad_1]
Google on Thursday introduced that it is searching for contributors to a brand new open supply initiative known as Graph for Understanding Artifact Composition, also referred to as GUAC, as a part of its ongoing efforts to beef up the software program provide chain.
“GUAC addresses a necessity created by the burgeoning efforts throughout the ecosystem to generate software program construct, safety, and dependency metadata,” Brandon Lum, Mihai Maruseac, and Isaac Hepworth of Google stated in a submit shared with The Hacker News.
“GUAC is supposed to democratize the supply of this safety data by making it freely accessible and helpful for each group, not simply these with enterprise-scale safety and IT funding.”
Software provide chain has emerged a profitable assault vector for menace actors, whereby exploiting only one weak point — as seen within the case of SolarWinds and Log4Shell — opens a pathway lengthy sufficient to traverse down the availability chain and steal delicate knowledge, plant malware, and take management of methods belonging to downstream prospects.
Google, final 12 months, launched a framework known as SLSA (quick for Supply chain Levels for Software Artifacts) that goals to make sure the integrity of software program packages and forestall unauthorized modifications.
It has additionally launched an up to date model of Security Scorecards, which identifies the chance third-party dependencies can introduce to a venture, permitting builders to make knowledgeable selections about accepting susceptible code or contemplating different options.
This previous August, Google additional launched a bug bounty program to determine safety vulnerabilities spanning a lot of tasks resembling Angular, Bazel, Golang, Protocol Buffers, and Fuchsia.
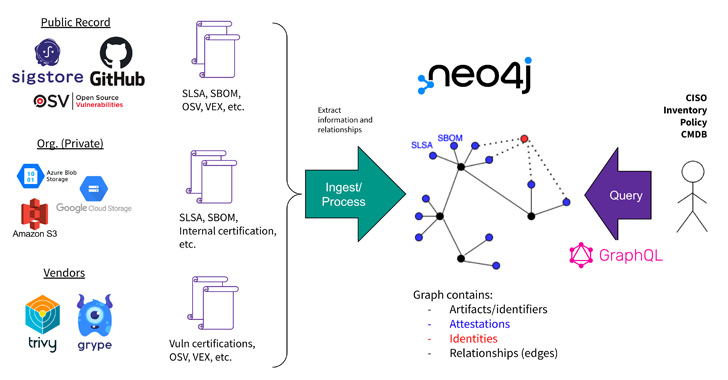
GUAC is the corporate’s newest effort to bolster the well being of the availability chain. It achieves this by aggregating software program safety metadata from a mixture of private and non-private sources right into a “data graph” that may reply questions on provide chain dangers.
The knowledge that undergirds this structure is derived from Sigstore, GitHub, Open Source Vulnerabilities (OSV), Grype, and Trivy, amongst others, to derive significant relationships between vulnerabilities, tasks, assets, builders, artifacts, and repositories.
“Querying this graph can drive higher-level organizational outcomes resembling audit, coverage, danger administration, and even developer help,” Google stated.
Put in a different way, the thought is to attach the totally different dots between a venture and its developer, a vulnerability and the corresponding software program model, and the artifact and the supply repository it belongs to.
The intention, due to this fact, is to not solely allow organizations to find out if they’re affected by a particular vulnerability, but additionally estimate the blast radius ought to the availability chain be compromised.
That stated, Google additionally seems to be cognizant of the potential threats that might undermine GUAC, together with eventualities the place the system is tricked into ingesting cast details about artifacts and their metadata, which it expects to mitigate by cryptographic verification of information paperwork.
“[GUAC] goals to fulfill the use case of being a monitor for public provide chain and safety paperwork in addition to for inner use by organizations to question details about artifacts that they use,” the web big famous.