[ad_1]

A brand new Mirai botnet variant tracked as ‘V3G4’ targets 13 vulnerabilities in Linux-based servers and IoT gadgets to make use of in DDoS (distributed denial of service) assaults.
The malware spreads by brute-forcing weak or default telnet/SSH credentials and exploiting hardcoded flaws to carry out distant code execution on the goal gadgets. Once a tool is breached, the malware infects the machine and recruits it into its botnet swarm.
The explicit malware was noticed in three distinct campaigns by researchers at Palo Alto Networks (Unit 42), who reported monitoring the malicious exercise between July 2022 and December 2022.
Unit 42 believes all three assault waves originate from the identical menace actor as a result of the hardcoded C2 domains comprise the identical string, the shell script downloads are related, and the botnet shoppers utilized in all assaults characteristic similar features.
V3G4 assaults start with the exploitation of one of many following 13 vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2012-4869: FreePBX Elastix distant command execution
- Gitorious distant command execution
- CVE-2014-9727: FRITZ!Box Webcam distant command execution
- Mitel AWC distant command execution
- CVE-2017-5173: Geutebruck IP Cameras distant command execution
- CVE-2019-15107: Webmin command injection
- Spree Commerce arbitrary command execution
- FLIR Thermal Camera distant command execution
- CVE-2020-8515: DrayTek Vigor distant command execution
- CVE-2020-15415: DrayTek Vigor distant command execution
- CVE-2022-36267: Airspan AirSpot distant command execution
- CVE-2022-26134: Atlassian Confluence distant command execution
- CVE-2022-4257: C-Data Web Management System command injection
.png)
After compromising the goal machine, a Mirai-based payload is dropped on the system and makes an attempt to hook up with the hardcoded C2 deal with.
The botnet additionally makes an attempt to terminate a set of processes from a hardcoded checklist, which incorporates different competing botnet malware households.
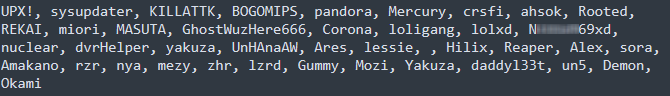
A attribute that differentiates V3G4 from most Mirai variants is that it makes use of 4 totally different XOR encryption keys as an alternative of only one, making reverse engineering the malware’s code and decoding its features more difficult.
When spreading to different gadgets, the botnet makes use of a telnet/SSH brute-forcer that tries to attach utilizing default or weak credentials. Unit 42 seen earlier malware variants used each telnet/SSH brute-forcing and vulnerability exploitation for spreading, whereas later samples didn’t use the scanner.
Finally, compromised gadgets are issued DDoS instructions straight from the C2, together with TCP, UDP, SYN, and HTTP flooding strategies.
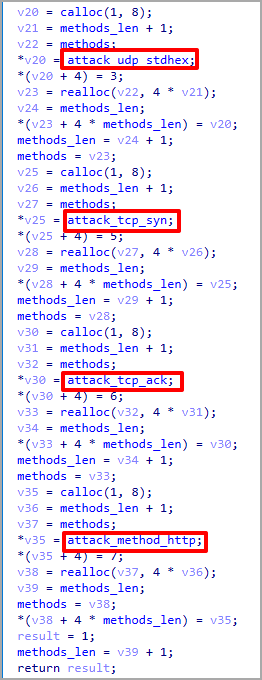
V3G4 seemingly sells DDoS providers to shoppers who wish to trigger service disruption to particular web sites or on-line providers.
However, this variant has not been tied to a selected service at the moment.
As all the time, one of the best ways to guard your gadgets from Mirai-like infections is to alter the default password and set up the most recent safety updates.
[ad_2]
