These ransomware infections on VMware ESXi software program are resulting from a vulnerability that has existed since 2021. Find out probably the most focused international locations and methods to safe your group.

Jump to:
How does this ransomware assault function?
CVE-2021-21974 is a vulnerability affecting OpenSLP as utilized in VMware ESXi. Successful exploitation of that vulnerability permits an attacker to execute arbitrary code, and exploits for this vulnerability could be present in numerous open sources since May 2021.
The French authorities’s Computer Emergency Response Team CERT-FR was the primary to elevate an alert on ransomware exploiting this vulnerability on Feb. 3, 2023, shortly adopted by French internet hosting supplier OVH.
Attackers can exploit the vulnerability remotely and unauthenticated through port 427 (Service Location Protocol, SLP), which is a protocol that the majority VMware clients don’t use.
The ransomware encrypts information with the next extensions on the affected methods: .vmdk, .vmxf, .vmsd, .vmsn, .vmss, .vswp, .nvram and .vmem. Then, it tries to close down the digital machines by killing the VMX course of to unlock the information.
A textual content be aware is left after encryption is finished (Figure A), asking for ransom that should be paid in Bitcoin cryptocurrency inside three days.
Figure A
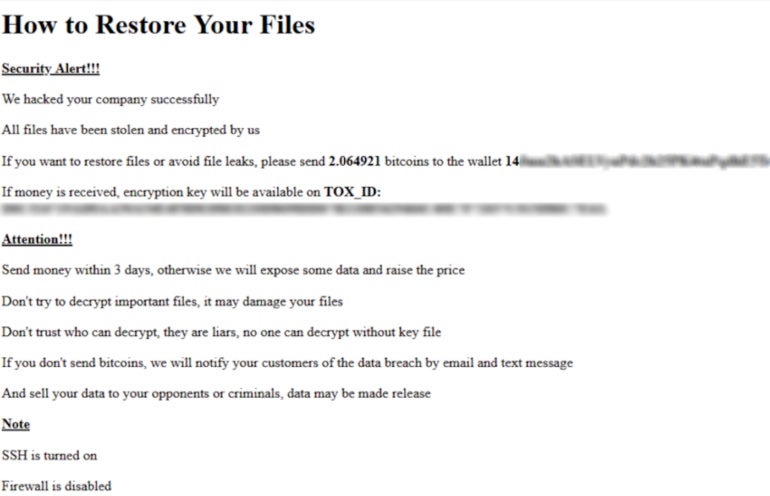
The ransomware risk actor behind this assault isn’t recognized, because the malware appears to be a brand new ransomware. OVH has reported that in response to a number of safety researchers, the encryption cipher used within the ransomware is identical as what was used within the leaked Babuk malware code from September 2021, though the code construction is totally different.
The Babuk code that leaked in 2021 has been used to create different malware that always targets ESXi methods, however it appears too early to attract a definitive conclusion as to the attribution of that new malware, which has been dubbed ESXiArgs by safety researchers.
France and U.S. are the largest targets
Censys Search, a web based instrument for looking out by means of internet-connected units, reveals that greater than 1,000 servers have been efficiently hit by the ransomware, principally in France, adopted by the U.S. and Germany.
At the time of writing, greater than 900 servers had been compromised in France, whereas roughly 400 servers within the U.S. had been hit.
Much more methods is perhaps weak and never but attacked. The Shadowserver Foundation reviews that round 27,000 situations could also be weak, in response to the model of its VMware software program.
How to guard your group from this ransomware risk
For methods working unpatched variations of VMware ESXi, absolutely the precedence is to chop the SLP service if it runs. The vulnerability can solely be exploited through that service, so whether it is closed, the system can’t be attacked through this vector.
The subsequent step consists of reinstalling the hypervisor in a model supported by VMware — ESXi 7.x or ESXi 8.x — and making use of all safety patches.
Finally, all administration providers needs to be protected and solely out there regionally. In case there’s a want for distant entry, VPN with multi-factor authentication or IP filtering needs to be used.
Jan Lovmand, chief know-how officer of BullWall, a cybersecurity agency targeted on stopping ransomware assaults, informed TechRepublic extra in regards to the vulnerability.
“A patch has been available from VMware since February 2021 when the vulnerability was discovered,” Lovmand mentioned. “This just goes to show how long it takes many organizations to get around to patch internal systems and applications, which is just one of many reasons why the criminals keep finding their way in. The attack surface is big, and preventative security solutions can be bypassed in a scenario like this if the vulnerability has not been patched.”
Lovmand additionally confused the significance of patching your networks.
“It’s 50-50 odds that your company will be successfully hit with ransomware in 2023,” he mentioned. “Security solutions cannot protect unpatched networks.”
How to get well from this ransomware risk
Security researchers Enes Somnez and Ahmet Aykac have offered a resolution to get well in case a system has been attacked by this ransomware.
The researchers clarify that the ransomware encrypts small information like .vmdk and .vmx however not the server-flat.vmdk file, which accommodates the precise information. Using this file, it’s attainable to do a fallback and get well info from the system.
Julien Levrard, chief info safety officer from OVHCloud, wrote that the strategy documented by Somnez and Aykac has been examined by OVH in addition to many safety specialists with success on a number of impacted servers, with a hit price of two/3. He added that “this procedure requires strong skills on ESXi environments.”
Disclosure: I work for Trend Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.
Read subsequent: Patch administration coverage (TechRepublic Premium)

