[ad_1]
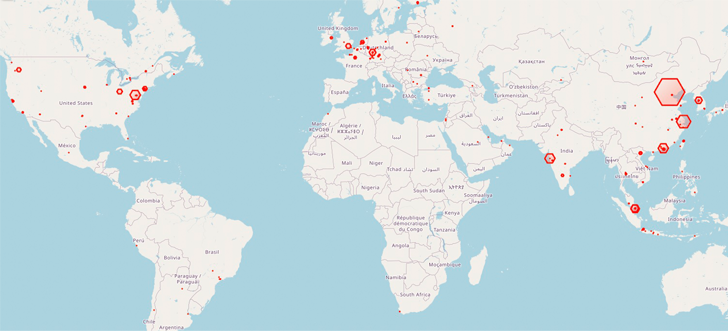
At least 1,200 Redis database servers worldwide have been corralled right into a botnet utilizing an “elusive and extreme risk” dubbed HeadCrab since early September 2021.
“This superior risk actor makes use of a state-of-the-art, custom-made malware that’s undetectable by agentless and conventional anti-virus options to compromise a lot of Redis servers,” Aqua safety researcher Asaf Eitani mentioned in a Wednesday report.
A major focus of infections has been recorded in China, Malaysia, India, Germany, the U.Ok., and the U.S. to this point. The origins of the risk actor are presently unknown.
The findings come two months after the cloud safety agency make clear a Go-based malware codenamed Redigo that has been discovered compromising Redis servers.
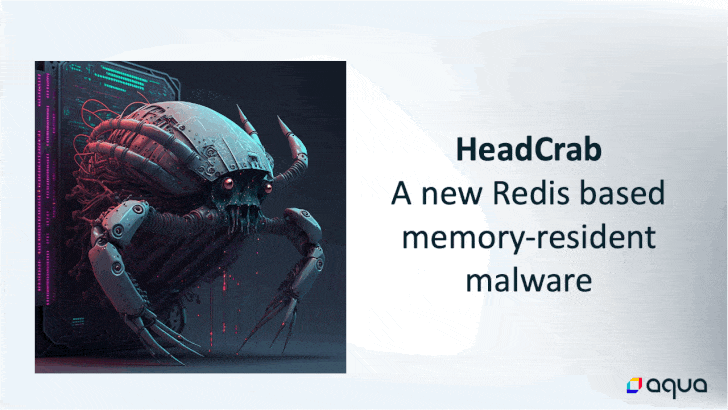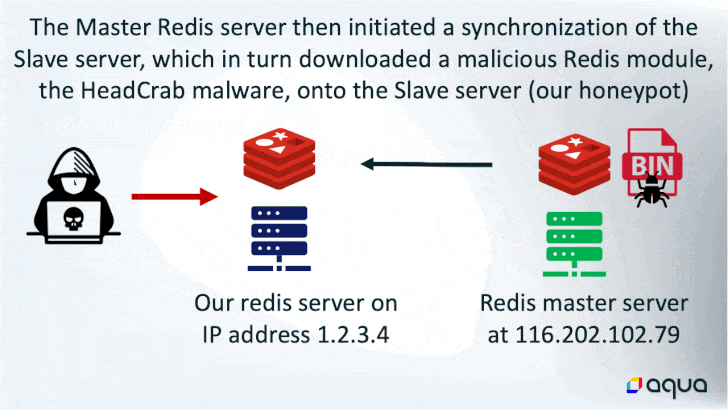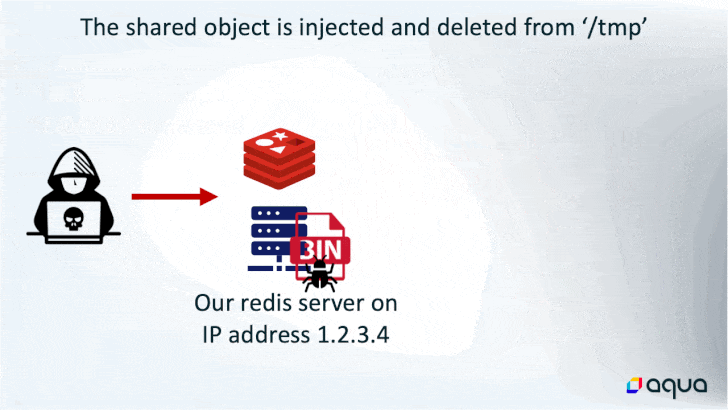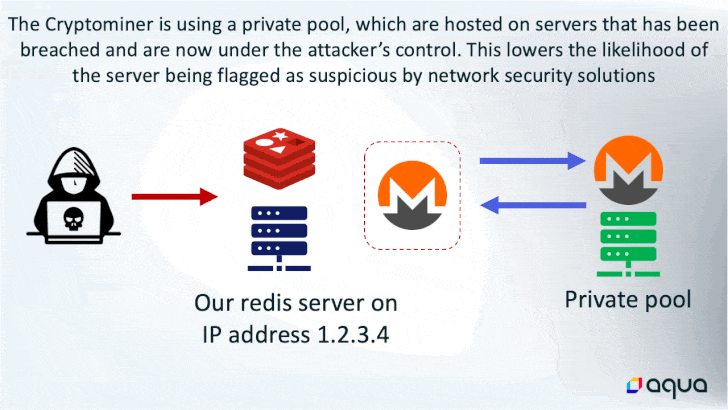
The assault is designed to focus on Redis servers which can be uncovered to the web, adopted by issuing a SLAVEOF command from one other Redis server that is already underneath the adversary’s management.
In doing so, the rogue “grasp” server initiates a synchronization of the newly hacked server to obtain the malicious payload, which comprises the delicate HeadCrab malware onto the latter.
“The attacker appears to primarily goal Redis servers and has a deep understanding and experience in Redis modules and APIs as demonstrated by the malware,” Eitani famous.
While the last word finish aim of utilizing the memory-resident malware is to hijack the system sources for cryptocurrency mining, it additionally boasts of quite a few different choices that permits the risk actor to execute shell instructions, load fileless kernel modules, and exfiltrate knowledge to a distant server.
What’s extra, a follow-on evaluation of the Redigo malware has revealed it to be weaponizing the identical master-slave approach for proliferation, and never the Lua sandbox escape flaw (CVE-2022-0543) as beforehand disclosed.
Users are really useful to chorus from exposing Redis servers on to the web, disable the “SLAVEOF” function of their environments if not in use, and configure the servers to solely settle for connections from trusted hosts.
Eitani mentioned “HeadCrab will persist in utilizing cutting-edge strategies to penetrate servers, both by means of exploiting misconfigurations or vulnerabilities.”
Update
Following the publication of the story, Redis shared the beneath assertion with The Hacker News –
Redis could be very supportive of the cybersecurity analysis neighborhood, and we wish to acknowledge AquaSec for getting this report out to learn the Redis neighborhood. Their report reveals the potential risks of mis-configuring Redis. We encourage all Redis customers to observe the safety steerage and greatest practices revealed inside our open supply and business documentation.
We ought to notice that there aren’t any indicators that Redis Enterprise software program or Redis Cloud providers have been impacted by these assaults.