[ad_1]
Since farmers started digging up historical bone fragments within the fields across the Yellow River in japanese China over 100 years in the past, researchers have been poring over the mysterious script discovered on them.
The script on the “oracle bones,” so referred to as as a result of they had been used to attempt to divine the long run, is the earliest recognized type of Chinese writing, courting again 3,000 years. But their examine has been difficult: the bones are fragile and fragmented, copies of the script made by ink rubbings could be blurry or incomplete and collections are scattered in nationwide museums and personal collections in China and world wide.
Now researchers in Beijing are utilizing AI to fast-track the essential however essential work of evaluating every script pattern with hundreds of others in databases. This work paves the way in which for researchers to decipher them and make clear all the pieces from the day by day issues of individuals in historical instances to how Chinese writing first developed.
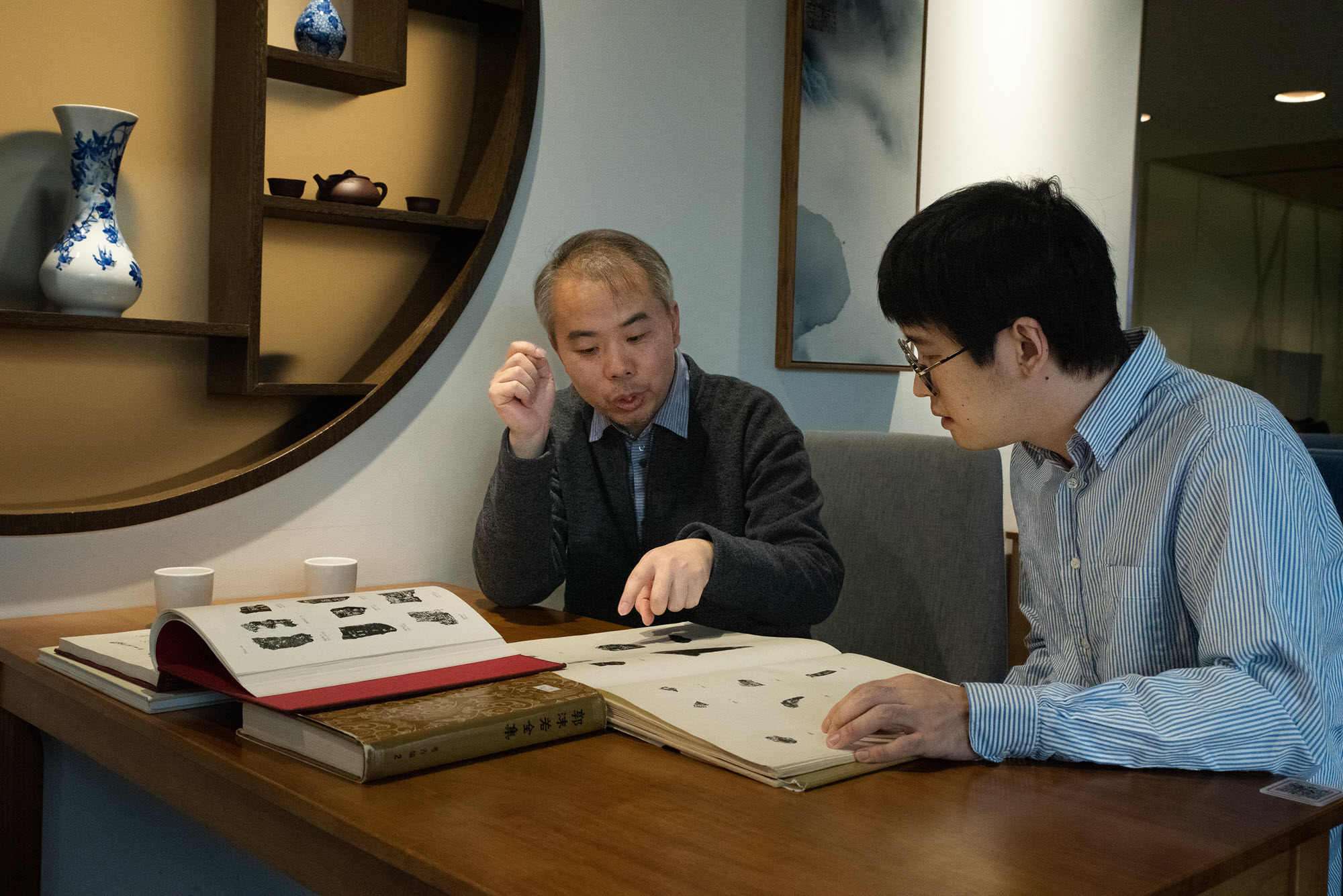
“This is a great example of human-machine collaboration,” mentioned Bofeng Mo, a professor from the Center for Oracle Bone Studies at Capital Normal University, who labored on the mission with Zhirong Wu, a senior researcher at Microsoft Research Asia.

Oracle bone inscriptions have been acknowledged by UNESCO’s International Memory of the World Register as a worthwhile report of the Shang folks from 1400 B.C. to 1100 B.C., along with being the earliest proof of a Chinese writing system. In China, each child learns in regards to the oracle bones at school.
Most of the bones had been excavated round Anyang City in Henan Province, about 500 kilometers (about 310 miles) southwest of Beijing. They had been often the scapula, or shoulder blades, of oxen or the stomach shells of turtles – each of which supply a flat floor for the script. During the Shang Dynasty, a bronze-age civilization, somebody would warmth the bones till they cracked. The sample of the cracks would provide steerage on issues round praying, royal and navy affairs, the climate, harvests and so forth.
Since 1899, about 150,000 items have been unearthed and are actually housed in additional than 100 institutes world wide, in line with consultants behind the UNESCO nomination. The largest collections are within the National Library of China, the Palace Museum and different Chinese establishments although oracle bones collections are discovered as distant because the Royal Scottish Museum and the Royal Ontario Museum in Canada.
The markings have each pictograph and textual content parts. With no equal of a Rosetta Stone as a information, scientists have solely deciphered about 1,000 of the roughly 4,000 characters recognized.

Up till now script examine has been painstakingly laborious. The earliest copies of oracle bone script had been made by Chinese ink rubbings and, extra just lately, pictures and 3D imaging know-how. Researchers needed to manually evaluate every picture to search out duplicates or overlaps, with the objective of sewing collectively fragments – like a jigsaw puzzle – right into a extra full entire for examine.
“Since a piece of oracle bone may have been recorded several times with different levels of clarity and integrity, a lot of work is need to relate, compare and interpret them,” Yubin Jiang, a researcher on the Research Center for Unearthed Documents and Ancient Characters at Fudan University, advised Microsoft. “In the past, this burden fell solely on the shoulders of scholars with rich experience and sharp memory, but their research only led to random findings.”
“Diviner has managed to complete wide-ranging duplication detection in a highly efficient, fruitful and exciting way,” he added.
Wu, the researcher at Microsoft, focuses on the nascent area of self-supervised studying, a kind of machine studying that doesn’t depend on folks to do guide labeling of information. He approached Mo a few yr in the past after listening to that the professor was experimenting with AI to review script. At the time, Mo was utilizing off-the-shelf picture recognition software program, which solely allowed just a few photos to be uploaded every time and required a consumer to select one as a reference picture.
“We developed the technology to train the Diviner model from scratch,” mentioned Wu.
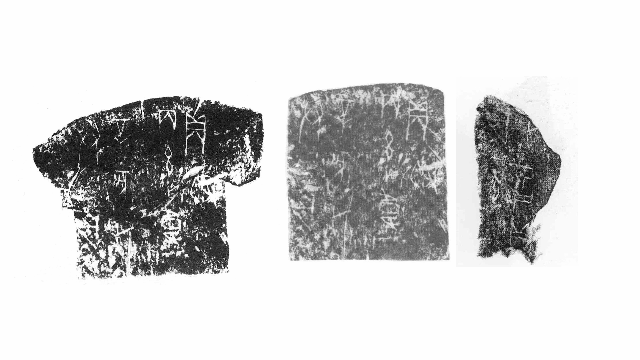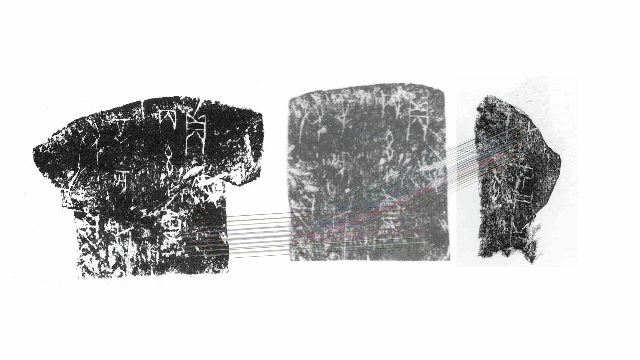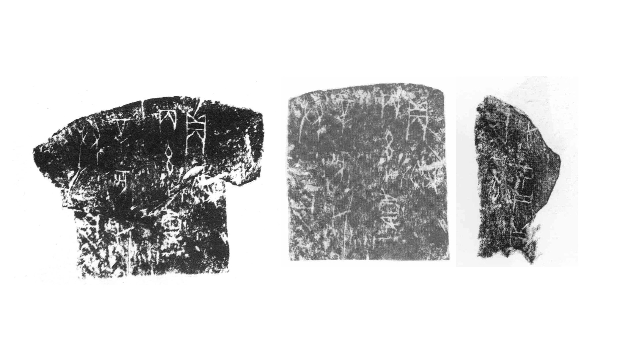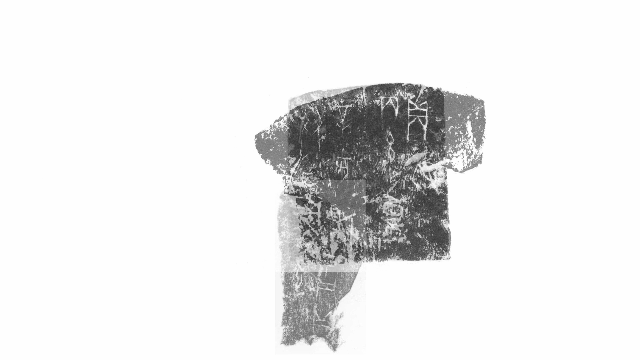
Wu mentioned he and one different crew member took eight to 9 months to construct the mannequin. In November 2022, within the area of 1 week, the Diviner Project in contrast 181,134 items of inscription rubbings throughout 100 databases. It not solely reproduced tens of hundreds of beforehand recognized duplicates discovered by folks but in addition discovered greater than 300 new pairs.
After Wu and Mo shared the outcomes on the web site of the Pre-Qin Research Office on the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, which has its personal substantial assortment of oracle bones, researchers at different establishments have reached out to them for assist, mentioned Wu. The mission was additionally featured in a particular oracle bones episode on nationwide broadcaster CCTV on January 2, 2023.
This is simply step one.
“The current project is to clean the data and recover the data to the original form by joining small fragments to the original big one,” mentioned Wu. “With this, we hope we can move on to the final challenge – deciphering the meaning of these characters.”
Those findings may have implications for various fields.
“To archaeologists, they are the cultural remains of humans. To historians, they are the historical material of the Shang Dynasty. To linguists, they are the earliest systemic Chinese characters,” mentioned Mo. Moreover, “records of solar eclipses, lunar eclipses and meteor showers found in oracle bone inscriptions can be merged with astronomy.”
Top picture: Zhirong Wu of Microsoft Research Asia makes use of AI to review historical Chinese script on oracle bones. Photo by Gilles Sabrie for Microsoft.
