[ad_1]
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causal agent of the coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has globally contaminated greater than 639 million people and claimed over 6.6 million lives. Despite the fast graduation of COVID-19 vaccination packages in most international locations internationally, the virus has remained in circulation. This is principally due to the continuous emergence of recent SARS-CoV-2 variants, such because the Omicron and Delta strains, which may escape immune responses induced by way of vaccination and pure an infection.
 Study: Longitudinal single-cell evaluation of SARS-CoV-2-reactive B cells uncovers persistence of early-formed, antigen particular clones
Study: Longitudinal single-cell evaluation of SARS-CoV-2-reactive B cells uncovers persistence of early-formed, antigen particular clones
Background
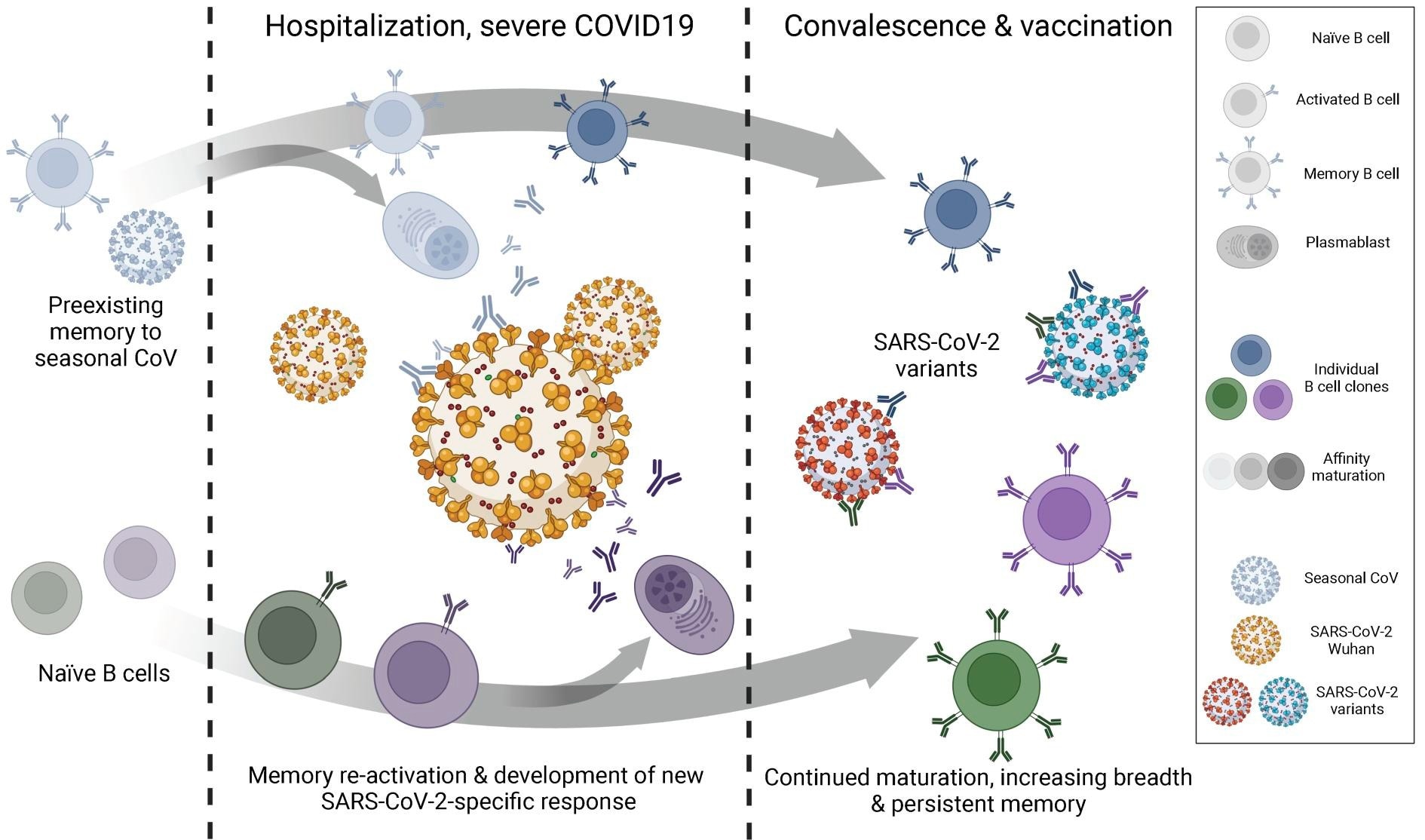
Many research have reported the era of early immune responses upon an infection. In severely contaminated COVID-19 sufferers, an elevated variety of Th1-like CD8 and CD4 cells, plasmablasts, erythroid cells, and megakaryocytes had been detected. Additionally, spike (S)-binding, neutralizing antibodies (Abs) of the IgA and IgG isotypes had been discovered within the early part of the an infection.
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants has drawn extra consideration to the research of reminiscence B cells (MBC). Animal mannequin research on influenza indicated that the MBC pool possesses a larger breadth of antigenic binding than the plasmablast response. This discovering implies that plasma cells and serum Abs shield in opposition to reinfection with the identical viral pressure, whereas the MBC pool can shield in opposition to a various vary of rising variants.
The evaluation of the MBC improvement after COVID-19 revealed an ongoing enhance of B cell receptor (BCR) mutations, which was at par with antigen persistence and persevering with germinal heart (GC) exercise. This growing variety of mutations additionally enhanced the neutralization breadth of the MBC pool.
The improvement of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) cloned from SARS-CoV-2 contaminated sufferers at completely different factors of an infection revealed appreciable neutralizing breadth in opposition to viral variants. However, longitudinal analysis inspecting the immune response of the identical sufferers throughout hospitalization, after restoration, and after vaccination is missing.
About the Study
A current JCI Insight research addressed this hole in analysis and utilized a longitudinal strategy to supply necessary insights into the evolution of B cells after viral infections. This research recruited six extreme/critically contaminated SARS-CoV-2 sufferers post-hospital admission at Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Sweden. They had been adopted via the illness development and restoration interval for as much as one 12 months.
The sufferers’ blood and serum samples had been collected each three days throughout hospitalization. In addition, post-discharge samples had been collected each three months for as much as one 12 months. Overall, 50% of the research cohort obtained COVID-19 vaccination by the tip of the follow-up interval.
The samples had been used to measure complete peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and B cells, primarily based on single cell transcriptomics, expression of floor proteins, antigen binding (Spike (S), Nucleocapsid (N) or Receptor Binding Domain (RBD)), and BCR sequences, at every of the analyzed time factors.
Study Findings
The longitudinal research design enabled scientists to hint the origin of antigen-specific B cells and perceive their evolution sample in every affected person. A big change within the circulating immune populations was noticed in the course of the an infection. During the early part of hospitalization, CD4 T cells with sturdy IFN signatures had been detected, which disappeared inside 3 months.
After 14 days of hospital admission, immune cell composition or transcriptional options stabilized. However, because of the small pattern measurement, it was difficult to make a agency conclusion concerning the affiliation between the analyzed immune responses, comorbidities, and normal immune standing.
Three sufferers with respiratory comorbidities didn’t reveal any important distinction within the variety of the completely different immune cell populations or B cells. Overall, no matter intercourse, comorbidities, age, and immune standing, an identical immune response was noticed in all sufferers.
After SARS-CoV-2 an infection, a major growth of B cell clones was not noticed; smaller clones had been detected in all samples at all-time factors, together with plasmablast. However, early plasmablasts didn’t persist for all the 12 months, even after vaccination. Notably, mAbs of the identical affected person, belonging to the identical clonal household, acquired an improved binding capability to completely different viral variants over time. This discovering implies persistent ongoing clonal affinity maturation.
Notably, after COVID-19 restoration, a major growth of MBC with elevated frequency of antigen-specific B cells and larger somatic hypermutation throughout binders had been noticed. COVID-19 vaccination didn’t speed up this course of. The findings of this research instructed that vaccination was not sufficient to induce sturdy clonal growth and reactivation of infection-derived MBC. However, analytical knowledge from sera revealed that after vaccination, a distinguished differentiation of MBC into Ab-secreting plasmablasts occurred.
A gene ontology evaluation revealed that switched immunoglobulin (swIg) MBC possessed a larger activated transcriptional signature than IgM MBC. Furthermore, it was discovered that RBD-specific swIg-MBC had been extra inclined to get reactivated upon reinfection.
Conclusions
In abstract, the present research revealed the presence of COVID-19 persisting clones that had been first induced after an infection. These clones had been maintained for as much as one 12 months whereas they improved their binding capability and neutralizing breath. In the longer term, extra analysis should be performed to grasp if comparable clones will be reactivated upon vaccination or reinfection.
