[ad_1]
In this interview, News-Medical talks to Dr Javier Yugueros-Marcos, Head of the Antimicrobial Resistance and Veterinary Products Department on the World Organisation for Animal Health, about how the world can work collectively to advertise the sustainable and accountable use of antimicrobials.
Please may you introduce your self and inform us about your function throughout the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)?
My identify is Javier Yugueros-Marcos, and I joined the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, based as OIE) one 12 months in the past in November 2021. I’m main the division answerable for the standard of veterinary merchandise, which encompasses diagnostics, vaccines and therapeutics, together with antimicrobials. Because of the significance of antimicrobials and antimicrobial resistance, about 80% of our exercise revolves round them.
We monitor antimicrobial use all around the world, develop requirements on the accountable and prudent use of antimicrobials, and assess the standard of actions within the subject in order that we will improve capacity-building and alter practices.
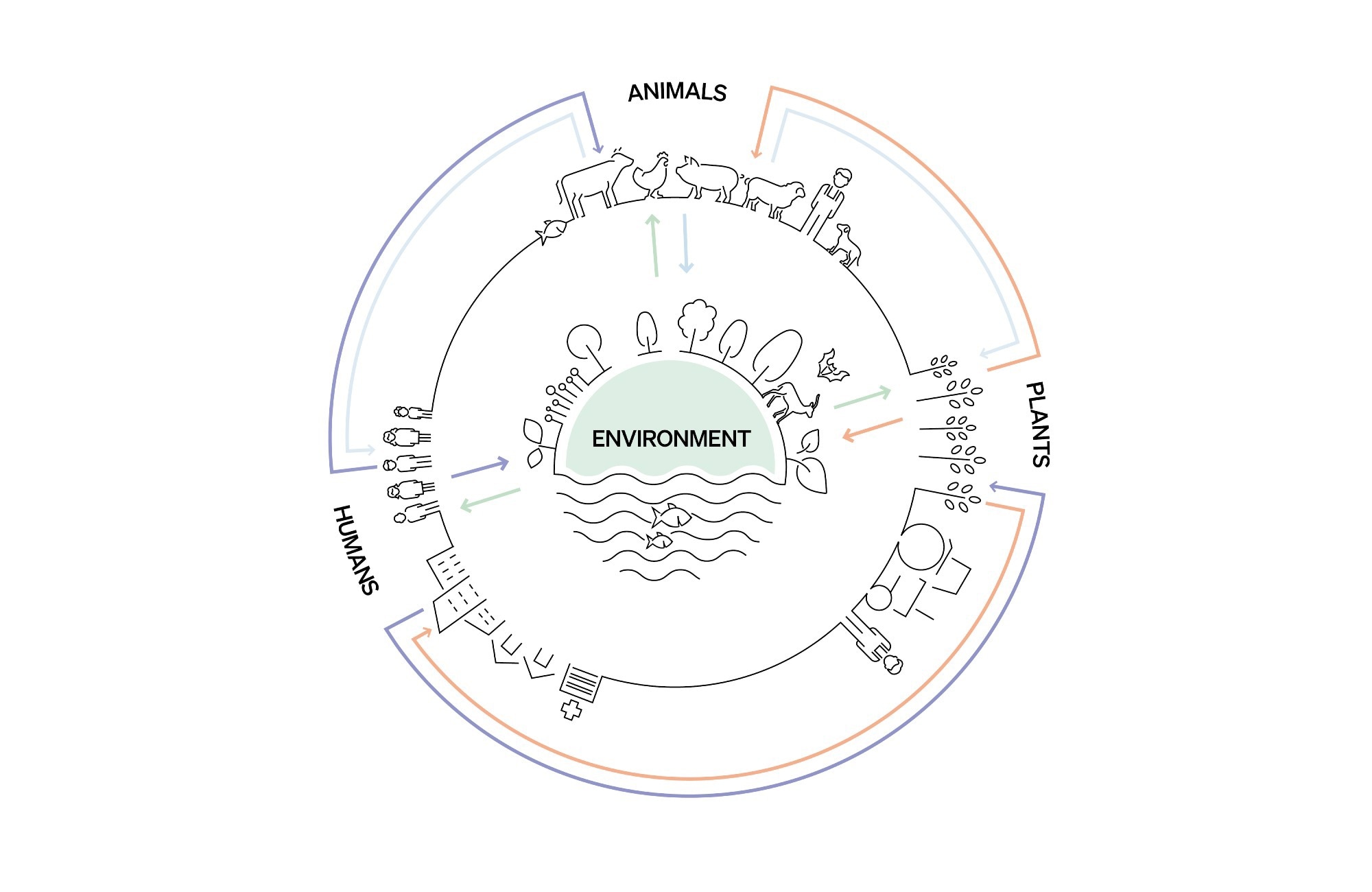
WOAH’s mission is to assist create a future through which people and animals profit and assist one another for a more healthy, extra sustainable world. Why is that this mission so vital given the present state of worldwide well being, and the way is the well being of people and animals interlinked?
Our work started in 1924 after an animal illness had a huge impact on meals safety: Rinderpest. Since then, we’ve got been engaged on enhancing animal well being worldwide, bringing about transparency by way of the standing of animal well being, and making certain protected worldwide commerce of animals and animal merchandise. All of this results in higher well being for people.
Today, the state of affairs shouldn’t be a lot completely different as a result of animal ailments nonetheless exist, and we nonetheless care about transparency and reporting animal illness outbreaks for protected worldwide commerce. However, human and animal well being are interlinked by way of extra than simply worldwide commerce. Let me offer you two examples.
One is zoonoses. It is estimated that 60% of infectious ailments in people originate from animals. This proportion is growing to 3 out of 4, when speaking about rising pathogens. Notable examples embrace Ebola virus, Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and the primary era of extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV). We suspect the identical for the extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus behind COVID-19, though we’ve got not recognized the intermediate species but, if ever.
It shouldn’t be solely food-producing animals that people danger contracting illness from, but additionally wildlife. And vice versa, as ailments may also be transmitted from people to animals. Human inhabitants growth is displacing animals from their atmosphere, and the brand new contact that people have with these displaced wild animals will increase the chance of zoonotic illness prevalence and transmission.
The second instance is antimicrobial resistance (AMR), which is the primary subject of this interview. Pathogens don’t have any borders, and the overuse and misuse of antimicrobials in any sector will instantly affect the others. When tackling this downside, it doesn’t make sense to watch the accountable use of antimicrobials in people if we don’t acquire the identical data in animals, and vice versa. Everything is linked. As lengthy as we don’t work collectively on this interconnected world, we will be unable to unravel its issues. It took us some time, however I feel that many stakeholders are lastly acknowledging that.
World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, based as OIE) – It’s Everyone’s Health.
Improving world well being and well-being can solely be achieved by additionally contemplating animals and the atmosphere. How will the development of animal well being consequently enhance the well being of people and the atmosphere?
Consider the examples I’ve simply given of infectious human ailments coming from animals. Improving animal well being will stop many of those occasions from taking place and can finally make sure that we’ve got a more healthy human sector. This consists of not solely food-producing animals and wildlife but additionally companion animals that are more and more current in our lives.
The different facet of all that is to contemplate how dependent we’re on animals for our livelihoods. Today, one out of 5 individuals rely on manufacturing animals for his or her revenue and livelihoods. This shouldn’t be so evident in high-income nations, however it’s extremely current in low and middle-income nations which symbolize an enormous proportion of the worldwide inhabitants.
Whenever we speak about animals, we have a tendency to consider terrestrial animals, however we even have to consider aquatic animals. Over 20 million individuals rely on the aquaculture sector. This is the quickest rising sector of these supplying protein for the world.
Every 12 months you and your companions on the WHO, the FAO and UNEP have a good time World Antimicrobial Awareness Week. The theme for 2022 is “Preventing Antimicrobial Resistance Together”. What does this theme imply to you?
There isn’t any more practical solution to keep away from antimicrobial misuse than using them solely when different approaches don’t work, solely when they’re mandatory. Prevention is the very first thing that we’ve got to keep in mind. We should maximise the applied sciences current as we speak to enhance biosecurity and guarantee best-in-class animal husbandry practices. One method that is properly underway is thru using vaccination throughout the sectors.
Before this, I used to be working within the human well being sector, so I’m accustomedto selling the time period ‘hygiene’. Hygiene is one of the simplest ways to stop an infection. And we’ve got seen this with the current COVID-19 pandemic, the place we employed social distancing, hand sanitizer use, and different measures. Thus, hygiene was enhanced. The similar applies for animals. And it’s not solely our arms that pose a danger – for instance, farm employees want to consider altering their boots after they go into the farm, and checking guests after they come onto the property.
All these components, in addition to how animals are raised and reside, have an effect on their capability to battle infections. Maximising their immunity prevents them from getting sick, stopping all of us from utilizing extra antimicrobials.
This is one thing that has been someway forgotten, and we want to emphasise this message. Simple and straightforward measures can save plenty of bother down the highway.

Image Credit: World Health Organization
With antimicrobial resistance being described by WHO as one of many prime 10 threats to world well being, what affect is it truly having on animals worldwide?
We want to be as superior as our colleagues from the human well being sector on this regard. Unfortunately, there’s at present no knowledge out there on the burden of antimicrobial resistance in animals at world degree, however we’re engaged on it.
There are a number of regional initiatives (i.e. Europe, Asia, Americas…) gathering knowledge on the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance within the animal well being sector. But as I mentioned, we don’t have any complete world knowledge but. Our colleagues from FAO are engaged on this. This 12 months they’ve began a pilot to gather knowledge on antimicrobial resistance in animals. They are starting in Asia, and their aim is to gather knowledge globally by the top of subsequent 12 months.
The different initiative that I wished to say is one which we’re main in collaboration with the University of Liverpool, which is named the Global Burden of Animal Diseases (or GBADs). It follows the identical methodology as one thing that was finished for people just a few years in the past. We have just lately developed a element on the financial affect of AMR in animals, significantly the socioeconomic affect on livelihoods the place antimicrobial resistance is current.
One key goal of World Antimicrobial Awareness Week is enhancing consciousness of AMR. Despite continued consciousness, many individuals nonetheless don’t totally perceive the broader implications it has not just for human well being, however for animal well being and environmental well being. What extra can individuals and policymakers do to proceed educating about this world well being menace?
There are a few staple items that we should preserve doing. One is repeating. Education is the straightforward train of repeating issues. Something that we’re beginning to work on is making the messages evolve and concentrating on populations the place the message can set off actions.
We have been discussing this with our Quadripartite colleagues (the Quadripartite alliance for One Health: FAO, UNEP, WHO and WOAH) just a few weeks in the past. One of the populations that have been recognized as highly effective drivers of communication is the youth and youngsters specifically. They be taught every part; they hearken to every part; they repeat every part that we will train them. They symbolize the longer term. If we reach educating them and making them perceive that antimicrobials don’t have to be overused or misused, then we might be reaching a degree of understanding that has not been gained till now.
In this regard, we’ve got already engaged with younger individuals and college students. For instance, we are going to take part within the upcoming Global AMR Youth Summit, organised by the World Health Students Alliance and going down in the course of the World Antimicrobial Awareness Week.
In phrases of concentrating on populations and adapting the messages, we’re at present engaged on renewing our net content material and making it extra comprehensible for non-technical populations, for instance, involved residents.
In phrases of the policymakers, the 2 actions wanted are 1) bringing them the info to showcase that there’s a downside, and a couple of) offering alternate options. It is then our accountability as an organisation to set requirements on how antimicrobials can be utilized responsibly and prudently. These suggestions are then used to information the event of nationwide laws or laws.
We are engaged on increasing the breadth of actions from food-producing animals to all animals, companion animals and wildlife included. We are making the function and the obligations of each actor throughout the chain a lot clearer, from the veterinary authorities to the farmer and pet house owners. We are offering these overarching rules that in the long run may be translated into laws or regulation, and subsequently have an motion within the subject. It can be inside our accountability to spotlight the precedence analysis areas for analysis businesses and nations to fund in order that in the long run we will present alternate options to antimicrobials.
©World Organisation for Animal Health
It has been described that to work collaboratively between sectors to deal with AMR, we have to use a One Health method. What is supposed by the time period One Health and what are its benefits for world well being?
One Health, in quite simple phrases, is about working collectively. We are all interconnected. What is going on within the animal well being sector is finally going to affect the human sector. And the behaviour of people has an affect on the animal well being sector, in addition to in meals methods and ecosystems.
Translated into the world of governments, One Health shouldn’t be far more than making all of the sectors work collectively. We try to advertise dialogue throughout sectors. At world degree, the Quadripartite organisations have realized to dialogue, work collectively, and undertake actions in collaboration.
How will this degree of worldwide collaboration, particularly between animal and human well being professionals, assist to deal with different issues akin to rabies?
AMR is a well being problem and it may be taken as a mannequin on how collaboration may enhance our response. The similar mannequin may be utilized to zoonotic ailments, people who might transmit from animals to people, or people to animals. When engaged on a human illness, if there’s an animal element, we have to choose up the telephone, write emails, and work with the division answerable for animal well being.
The Quadripartite organisations have been working collectively on AMR since 2014/15. Today, AMR is one motion monitor of the One Health joint motion plan, which has been just lately launched to advance One Health at world, regional and nationwide ranges. Our expertise may be an asset to different individuals working in comparable areas. AMR is a mannequin, after which the mannequin may be utilized to different shared well being challenges.
Alongside your present work surrounding antimicrobial resistance, what are another priorities you’re at present addressing inside WOAH?
Our AMR technique has 4 pillars: consciousness, surveillance and analysis, capacity-building, and requirements implementation.
In phrases of consciousness, this dialog is an effective instance. The World Antimicrobial Awareness Week, a world marketing campaign to boost consciousness and understanding of AMR and promote greatest practices amongst One Health stakeholders.
In phrases of surveillance, we’ve got plenty of fascinating issues ongoing. One is our database of worldwide antimicrobial use in animals, launched in 2015. For seven years, we’ve got been utilizing paper-based and Excel varieties to gather the data from nations. This 12 months marks a turning level, as final September we launched a very digitalised system to permit nations to report and use their knowledge for their very own actions. The platform will grow to be accessible for the general public within the upcoming 12 months.
At the identical time, we’re initiating an identical system for the detection of falsified and sub-standard merchandise. The keys to antimicrobial stewardship are having the best antimicrobial for the best particular person, on the proper time, with the best dose, and for the best interval. But it is usually vital to have the best product, as a result of if merchandise are falsified or sub-standard, inoculations are usually not going to have any efficacy, main finally to resistance. We are beginning a pilot expertise for a world system for alerting sub-standard and falsified merchandise.
The different initiative that we’ve got is the estimation of the financial burden of AMR. In phrases of analysis, we’re working with our Quadripartite companions, creating a One Health analysis precedence agenda in collaboration with many various stakeholders. The aim is to supply a roadmap of priorities that needs to be tackled by way of analysis from the One Health perspective.
Then, by way of capacity-building, we assist the Multi-Partner Trust Fund initiative in collaboration with our Quadripartite companions and the donors, which is as we speak funding 10 low- and middle-income nations to implement their nationwide motion plans on AMR utilizing a One Health method. We have realized to speak to one another at world degree, and we’re scaling up these efforts at native degree in order that the Minister of Agriculture, the Minister of Health, the Minister of Environment, and the Minister of Aquaculture in a given nation can do the identical to efficiently implement nationwide motion plans on AMR throughout the sectors. Kenya, Zimbabwe, Tajikistan and Morocco are examples of nations supported by way of this fund.
Last however not least, a powerful authorized framework is important if nations are to take efficient motion within the face of well being threats akin to AMR In addition to offering Standards on the accountable use of antimicrobials, we even have a programme on Veterinary Legislation Support (VLSP) that helps Members recognise and handle their wants for clear, complete veterinary laws.

Image Credit: Pressmaster/Shutterstock.com
Are you hopeful that with this continued consciousness, schooling and funding surrounding AMR, we are going to someday see a world with out AMR?
I want I may think about such a world, however all organisms on Earth share the identical planet and we’re all linked. We all adapt to our surroundings. Antimicrobial resistance is a pure phenomenon that microorganisms implement to evolve in a hostile, poisonous atmosphere. As quickly as they see an antimicrobial agent stopping them from thriving, they will develop resistance. Alexander Fleming warned us all when he acquired his Nobel prize. With each new antimicrobial that we’ve got developed, sooner slightly than later, resistance has appeared.
A world with out antimicrobial resistance is tough to think about. However, we will learn to reside in a world the place we will use antimicrobials sustainably and scale back the burden of human, animal and plant ailments. This is what we’re engaged on. We are engaged on making each actor within the animal well being sector conscious that we should use antimicrobials responsibly to make sure they continue to be out there for future generations.
Sustainability may be achieved by creating new antimicrobials, but additionally, extra importantly, by utilizing those that we’ve got as we speak responsibly.
This is the place motion for prevention is basically vital. If we encourage hygiene, enhance safety at farms, and preserve animals in good circumstances in order that they’ve a powerful immune system, then we will battle this battle and preserve low ranges of antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrobials should be used responsibly and sustainably.
With the COVID-19 pandemic reminding us that every one sectors should work collectively to realize scientific progress, we’ve got seen important developments in recent times, particularly inside illness diagnostics. Are there any specific fields inside animal well being that you’re excited to observe evolve over the approaching years?
I feel COVID-19 has additionally taught us concerning the energy of vaccination. I hope that after the pandemic everybody will perceive its significance by way of prevention. Hopefully, it’ll assist encourage belief and confidence on this follow.
Regarding diagnostics, I’m somewhat biased, as a result of I labored for 18 years within the subject of diagnostics, and, as a former colleague used to say, “without diagnosis, medicine is blind”. This is true for the human well being sector, however much more so for the animal well being sector, which is severely impacted by the dearth of diagnostic instruments, significantly modern ones. I hope that this space might be bolstered, due to growth in human well being being imparted into the animal well being sector.
What is subsequent for you and your work at WOAH? Are you concerned in any thrilling upcoming tasks?
I’ve talked about a number of already, however I’ll choose the three most fun ones.
First, the launch of the worldwide database on antimicrobial use in animals, known as ANIMUSE.
The world burden of animal ailments can be an thrilling undertaking as a result of it’ll give us an thought of the socioeconomic affect of animal ailments. I feel it’ll assist mobilise assets and ratify the significance of AMR within the animal well being sector.
Finally, the revision of requirements we’re endeavor. We are increasing the content material to different animals, not solely food-producing animals, and clarifying the obligations of each actor to make use of antimicrobials responsibly. I’m very assured that this can assist in the sector if individuals know who does what and learn how to do it correctly.
About Javier Y. Marcos
Javier Y. Marcos has a stable historical past of working in antimicrobial resistance (AMR), with eighteen years of expertise within the growth and commercialisation of diagnostics checks for infectious ailments, each for human and animal well being. Having graduated as a Doctor in Veterinary Medicine in 1997, he additionally holds a PhD in Microbiology & Molecular Biology from the Leon University, Spain.
At the top of 2021, he was appointed as Head of the AMR & Veterinary Products Department on the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, based as OIE), being accountable for the improved high quality of veterinary medicinal merchandise, and the coordination of actions supporting a accountable and prudent use of antimicrobials in animal well being worldwide.
