[ad_1]
A phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform often called Robin Banks has relocated its assault infrastructure to DDoS-Guard, a Russian supplier of bulletproof internet hosting companies.
The swap comes after “Cloudflare disassociated Robin Banks phishing infrastructure from its companies, inflicting a multi-day disruption to operations,” in response to a report from cybersecurity firm IronNet.
Robin Banks was first documented in July 2022 when the platform’s skills to supply ready-made phishing kits to prison actors have been revealed, making it potential to steal the monetary data of consumers of fashionable banks and different on-line companies.
It was additionally discovered to immediate customers to enter Google and Microsoft credentials on rogue touchdown pages, suggesting an try on a part of the malware authors to monetize preliminary entry to company networks for post-exploitation actions corresponding to espionage and ransomware.
In current months, Cloudflare’s resolution to blocklist its infrastructure within the wake of public disclosure has prompted the Robin Banks actor to maneuver its frontend and backend to DDoS-Guard, which has previously hosted the alt-tech social community Parler and the infamous Kiwi Farms.
“This internet hosting supplier can also be infamous in not complying with takedown requests, thus making it extra interesting within the eyes of risk actors,” the researchers famous.
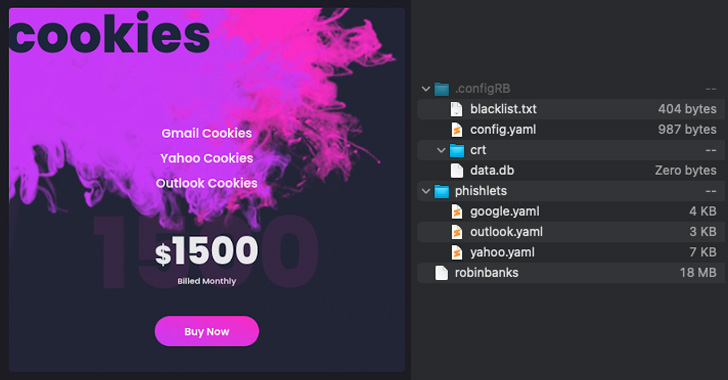
Chief among the many new updates launched is a cookie-stealing performance, in what’s seen as an try and serve a broader clientele corresponding to superior persistent risk (APT) teams that need to compromise particular enterprise environments. It’s provided for $1,500 monthly.
This is achieved by reusing code from evilginx2, an open supply adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) assault framework employed to steal credentials and session cookies from Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft Outlook even on accounts which have multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled.
Robin Banks can also be mentioned to have integrated a brand new safety measure that requires its prospects to activate two-factor authentication (2FA) to view the stolen data by way of the service, or, alternatively, obtain the information via a Telegram bot.
Another notable function is its use of Adspect, an advert fraud detection service, to redirect targets of phishing campaigns to rogue web sites, whereas main scanners and undesirable visitors to benign web sites to slide below the radar.
The findings are simply the newest in a collection of recent PhaaS companies which have emerged within the risk panorama, together with Frappo, EvilProxy, and Caffeine, making cybercrime extra accessible to newbie and skilled unhealthy actors alike.
What’s extra, the enhancements additionally illustrate the rising want for risk actors to depend on completely different strategies corresponding to AiTM and immediate bombing (aka MFA fatigue) – as lately noticed within the case of Uber – to avoid safety measures and achieve preliminary entry.
“The infrastructure of the Robin Banks phishing package depends closely on open-source code and off-the-shelf tooling, serving as a chief instance of the decreasing barrier-to-entry to not solely conducting phishing assaults, but additionally to making a PhaaS platform for others to make use of,” the researchers mentioned.