[ad_1]
Microsoft is warning of an uptick within the nation-state and prison actors more and more leveraging publicly-disclosed zero-day vulnerabilities for breaching goal environments.
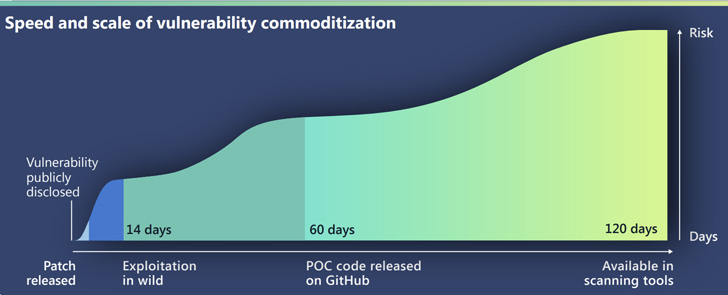
The tech large, in its 114-page Digital Defense Report, mentioned it has “noticed a discount within the time between the announcement of a vulnerability and the commoditization of that vulnerability,” making it crucial that organizations patch such exploits in a well timed method.
This additionally corroborates an April 2022 advisory from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), which discovered that dangerous actors are “aggressively” concentrating on newly disclosed software program bugs in opposition to broad targets globally.
Microsoft famous that it solely takes 14 days on common for an exploit to be out there within the wild after public disclosure of a flaw, stating that whereas zero-day assaults are initially restricted in scope, they are typically swiftly adopted by different menace actors, resulting in indiscriminate probing occasions earlier than the patches are put in.
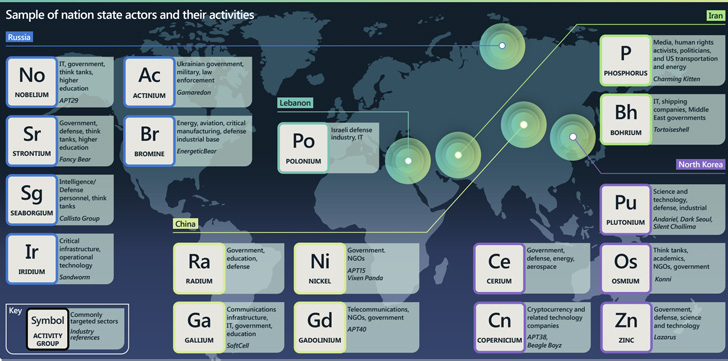
It additional accused Chinese state-sponsored teams of being “significantly proficient” at discovering and growing zero-day exploits.
This has been compounded by the truth that the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) enacted a brand new vulnerability reporting regulation in September 2021 that requires safety flaws to be reported to the federal government previous to them being shared with the product builders.
Redmond additional mentioned the regulation may allow government-backed components to stockpile and weaponize the reported bugs, resulting in the elevated use of zero-days for espionage actions designed to advance its financial and army pursuits.
Some of the vulnerabilities that have been first exploited by Chinese actors earlier than being picked up different adversarial teams embody –
- CVE-2021-35211 (CVSS rating: 10.0) – A distant code execution flaw in SolarWinds Serv-U Managed File Transfer Server and Serv-U Secure FTP software program that was exploited by DEV-0322.
- CVE-2021-40539 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – An authentication bypass flaw in Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus that was exploited by DEV-0322 (TiltedTemple).
- CVE-2021-44077 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – An unauthenticated distant code execution flaw in Zoho ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus that was exploited by DEV-0322 (TiltedTemple).
- CVE-2021-42321 (CVSS rating: 8.8) – A distant code execution flaw in Microsoft Exchange Server that was exploited three days after it was revealed in the course of the Tianfu Cup hacking contest on October 16-17, 2021.
- CVE-2022-26134 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – An Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) injection flaw in Atlassian Confluence that is prone to have been leveraged in opposition to an unnamed U.S. entity days earlier than the flaw’s disclosure on June 2.
The findings additionally come nearly a month after CISA launched a listing of high vulnerabilities weaponized by China-based actors since 2020 to steal mental property and develop entry into delicate networks.
“Zero-day vulnerabilities are a very efficient means for preliminary exploitation and, as soon as publicly uncovered, vulnerabilities may be quickly reused by different nation state and prison actors,” the corporate mentioned.