[ad_1]
In June 2021, we requested the recipients of our Data & AI Newsletter to reply to a survey about compensation. The outcomes gave us perception into what our subscribers are paid, the place they’re positioned, what industries they work for, what their considerations are, and what kinds of profession improvement alternatives they’re pursuing.
While it’s sadly untimely to say that the survey passed off on the finish of the COVID-19 pandemic (although we are able to all hope), it passed off at a time when restrictions had been loosening: we had been beginning to exit in public, have events, and in some instances even attend in-person conferences. The outcomes then present a spot to start out fascinated about what impact the pandemic had on employment. There was a variety of uncertainty about stability, notably at smaller corporations: Would the corporate’s enterprise mannequin proceed to be efficient? Would your job nonetheless be there in a yr? At the identical time, staff had been reluctant to search for new jobs, particularly if they’d require relocating—at the very least in keeping with the rumor mill. Were these considerations mirrored in new patterns for employment?
Executive Summary
- The common wage for information and AI professionals who responded to the survey was $146,000.
- The common change in compensation during the last three years was $9,252. This corresponds to an annual enhance of two.25%. However, 8% of the correspondents reported decreased compensation, and 18% reported no change.
- We don’t see proof of a “great resignation.” 22% of respondents stated they supposed to alter jobs, roughly what we might have anticipated. Respondents appeared involved about job safety, most likely due to the pandemic’s impact on the economic system.
- Average compensation was highest in California ($176,000), adopted by Eastern Seaboard states like New York and Massachusetts.
- Compensation for ladies was considerably decrease than for males (84%). Salaries had been decrease no matter training or job title. Women had been extra doubtless than males to have superior levels, notably PhDs.
- Many respondents acquired certifications. Cloud certifications, particularly in AWS and Microsoft Azure, had been most strongly related to wage will increase.
- Most respondents participated in coaching of some kind. Learning new expertise and bettering outdated ones had been the commonest causes for coaching, although hireability and job safety had been additionally components. Company-provided coaching alternatives had been most strongly related to pay will increase.
Demographics
The survey was publicized by way of O’Reilly’s Data & AI Newsletter and was restricted to respondents within the United States and the United Kingdom. There had been 3,136 legitimate responses, 2,778 from the US and 284 from the UK. This report focuses on the respondents from the US, with solely restricted consideration paid to these from the UK. A small variety of respondents (74) recognized as residents of the US or UK, however their IP addresses indicated that they had been positioned elsewhere. We didn’t use the information from these respondents; in apply, discarding this information had no impact on the outcomes.
Of the two,778 US respondents, 2,225 (81%) recognized as males, and 383 (14%) recognized as girls (as recognized by their most well-liked pronouns). 113 (4%) recognized as “other,” and 14 (0.5%) used “they.”
The outcomes are biased by the survey’s recipients (subscribers to O’Reilly’s Data & AI Newsletter). Our viewers is especially sturdy within the software program (20% of respondents), pc {hardware} (4%), and pc safety (2%) industries—over 25% of the overall. Our viewers can also be sturdy within the states the place these industries are concentrated: 42% of the US respondents lived in California (20%), New York (9%), Massachusetts (6%), and Texas (7%), although these states solely make up 27% of the US inhabitants.
Compensation Basics
The common annual wage for workers who labored in information or AI was $146,000. Most salaries had been between $100,000 and $150,000 yearly (34%); the following most typical wage tier was from $150,000 to $200,000 (26%). Compensation depended strongly on location, with common salaries highest in California ($176,000).
The common wage change over the previous three years was $9,252, which is 2.25% per yr (assuming a remaining wage equal to the common). A small variety of respondents (8%) reported wage decreases, and 18% reported no change. Economic uncertainty brought on by the pandemic could also be answerable for the declines in compensation. 19% reported will increase of $5,000 to $10,000 over that interval; 14% reported will increase of over $25,000. A research by the IEEE means that the common wage for technical staff elevated 3.6% per yr, larger than our respondents indicated.
39% of respondents reported promotions up to now three years, and 37% reported altering employers throughout that interval. 22% reported that they had been contemplating altering jobs as a result of their salaries hadn’t elevated through the previous yr. Is this an indication of what some have referred to as a “great resignation”? Common knowledge has it that technical staff change jobs each three to 4 years. LinkedIn and Indeed each suggest staying for at the very least three years, although they observe that youthful staff change jobs extra usually. LinkedIn elsewhere states that the annual turnover charge for know-how staff is 13.2%—which means that staff keep at their jobs for roughly seven and a half years. If that’s right, the 37% that modified jobs over three years appears about proper, and the 22% who stated they “intend to leave their job due to a lack of compensation increase” doesn’t appear overly excessive. Keep in thoughts that intent to alter and precise change will not be the identical—and that there are a lot of causes to alter jobs other than wage, together with flexibility round working hours and dealing from dwelling.
64% of the respondents took half in coaching or obtained certifications up to now yr, and 31% reported spending over 100 hours in coaching applications, starting from formal graduate levels to studying weblog posts. As we’ll see later, cloud certifications (particularly in AWS and Microsoft Azure) had been the preferred and appeared to have the biggest impact on salaries.
The causes respondents gave for taking part in coaching had been surprisingly constant. The overwhelming majority reported that they needed to be taught new expertise (91%) or enhance current expertise (84%). Data and AI professionals are clearly occupied with studying—and that studying is self-motivated, not imposed by administration. Relatively few (22%) stated that coaching was required by their job, and even fewer participated in coaching as a result of they had been involved about shedding their job (9%).
However, there have been different motives at work. 56% of our respondents stated that they needed to extend their “job security,” which is at odds with the low quantity who had been involved about shedding their job. And 73% reported that they engaged in coaching or obtained certifications to extend their “hireability,” which can recommend extra concern about job stability than our respondents would admit. The pandemic was a risk to many companies, and staff had been justifiably involved that their job may vanish after a foul pandemic-influenced quarter. A want for elevated hireability might also point out that we’ll see extra folks trying to change jobs within the close to future.
Finally, 61% of the respondents stated that they participated in coaching or earned certifications as a result of they needed a wage enhance or a promotion (“increase in job title/responsibilities”). It isn’t shocking that staff see coaching as a path to promotion—particularly as corporations that need to rent in fields like information science, machine studying, and AI take care of a scarcity of certified staff. Given the problem of hiring experience from outdoors, we anticipate an growing variety of corporations to develop their very own ML and AI expertise internally utilizing coaching applications.
Salaries by Gender
To no one’s shock, our survey confirmed that information science and AI professionals are largely male. The variety of respondents tells the story by itself: solely 14% recognized as girls, which is decrease than we’d have guessed, although it’s roughly in keeping with our convention attendance (again after we had stay conferences) and roughly equal to different technical fields. A small quantity (5%) reported their most well-liked pronoun as “they” or Other, however this pattern was too small to attract any important comparisons about compensation.
Women’s salaries had been sharply decrease than males’s salaries, averaging $126,000 yearly, or 84% of the common wage for males ($150,000). That differential held no matter training, as Figure 1 reveals: the common wage for a girl with a doctorate or grasp’s diploma was 82% of the wage for a person with an equal diploma. The distinction wasn’t fairly as excessive for folks with bachelor’s levels or who had been nonetheless college students, however it was nonetheless important: girls with bachelor’s levels or who had been college students earned 86% or 87% of the common wage for males. The distinction in salaries was best between individuals who had been self-taught: in that case, girls’s salaries had been 72% of males’s. An affiliate’s diploma was the one diploma for which girls’s salaries had been larger than males’s.
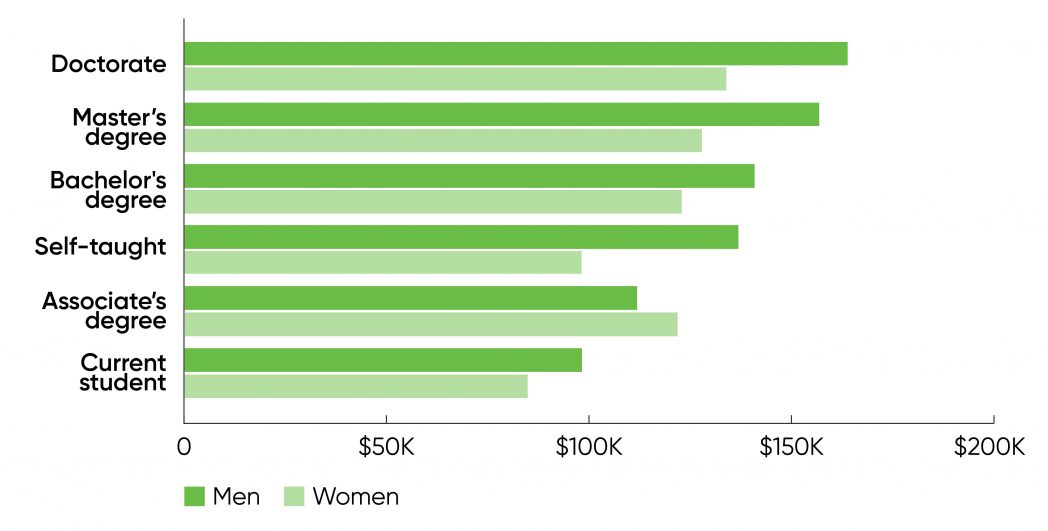
Despite the wage differential, the next share of girls had superior levels than males: 16% of girls had a doctorate, versus 13% of males. And 47% of girls had a grasp’s diploma, versus 46% of males. (If these percentages appear excessive, remember that many professionals in information science and AI are escapees from academia.)
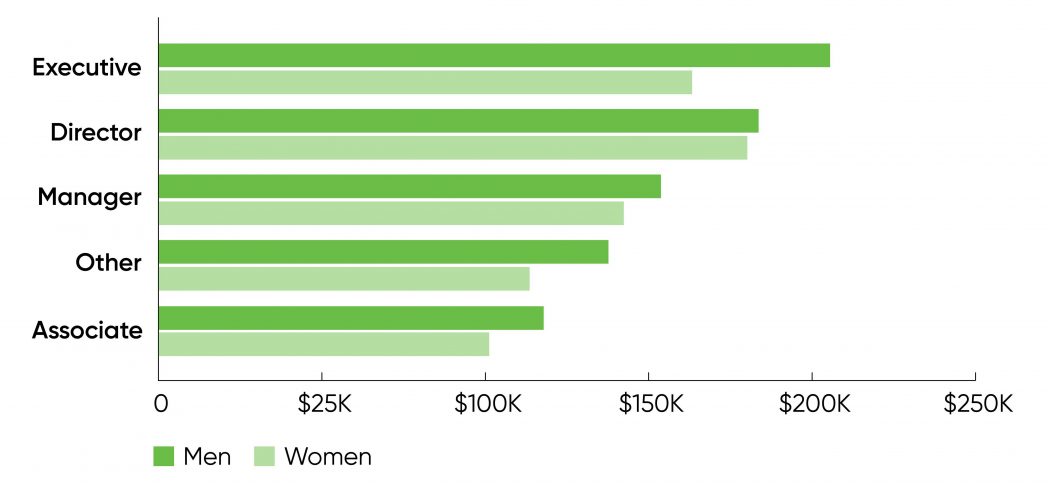
Women’s salaries additionally lagged males’s salaries after we in contrast men and women with related job titles (see Figure 2). At the chief degree, the common wage for ladies was $163,000 versus $205,000 for males (a 20% distinction). At the director degree, the distinction was a lot smaller—$180,000 for ladies versus $184,000 for males—and ladies’s salaries had been really larger than these on the government degree. It’s simple to hypothesize about this distinction, however we’re at a loss to clarify it. For managers, girls’s salaries had been $143,000 versus $154,000 for males (a 7% distinction).
Career development can also be a difficulty: 18% of the ladies who participated within the survey had been executives or administrators, in contrast with 23% of the boys.
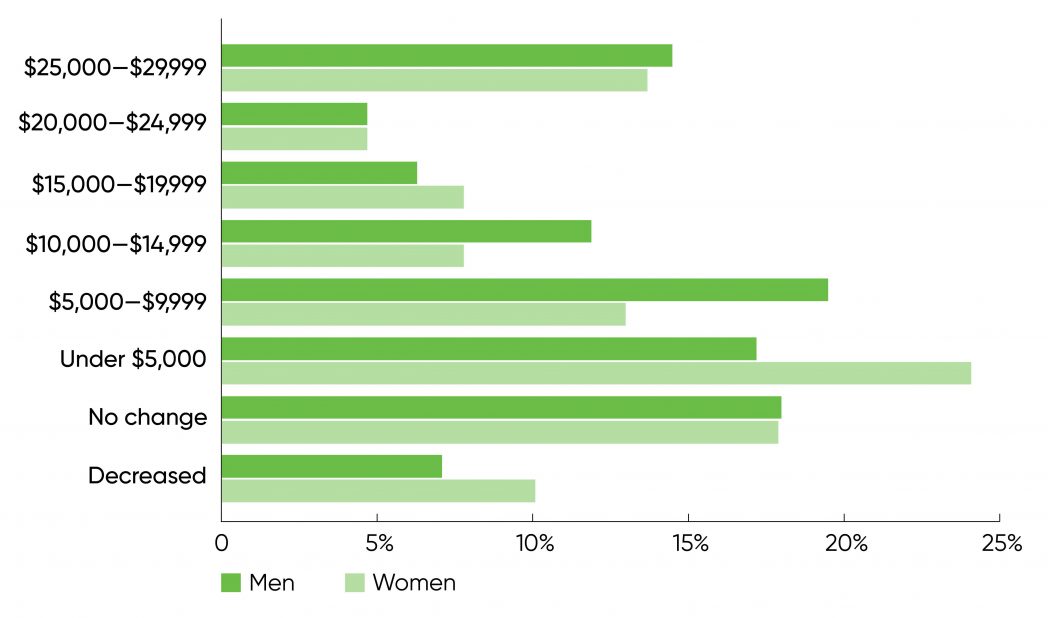
Before shifting on from our consideration of the impact of gender on wage, let’s take a quick take a look at how salaries modified over the previous three years. As Figure 3 reveals, the share of women and men respondents who noticed no change was just about equivalent (18%). But extra girls than males noticed their salaries lower (10% versus 7%). Correspondingly, extra males noticed their salaries enhance. Women had been additionally extra more likely to have a smaller enhance: 24% of girls had a rise of beneath $5,000 versus 17% of males. At the excessive finish of the wage spectrum, the distinction between women and men was smaller, although nonetheless not zero: 19% of males noticed their salaries enhance by over $20,000, however solely 18% of girls did. So probably the most important variations had been within the midrange. One anomaly stands out: a barely larger share of girls than males obtained wage will increase within the $15,000 to $20,000 vary (8% versus 6%).
Salaries by Programming Language
When we checked out the preferred programming languages for information and AI practitioners, we didn’t see any surprises: Python was dominant (61%), adopted by SQL (54%), JavaScript (32%), HTML (29%), Bash (29%), Java (24%), and R (20%). C++, C#, and C had been additional again within the checklist (12%, 12%, and 11%, respectively).
Discussing the connection between programming languages and wage is hard as a result of respondents had been allowed to examine a number of languages, and most did. But after we regarded on the languages related to the very best salaries, we bought a considerably totally different checklist. The most generally used and fashionable languages, like Python ($150,000), SQL ($144,000), Java ($155,000), and JavaScript ($146,000), had been solidly in the course of the wage vary. The outliers had been Rust, which had the very best common wage (over $180,000), Go ($179,000), and Scala ($178,000). Other much less frequent languages related to excessive salaries had been Erlang, Julia, Swift, and F#. Web languages (HTML, PHP, and CSS) had been on the backside (throughout $135,000). See Figure 4 for the complete checklist.
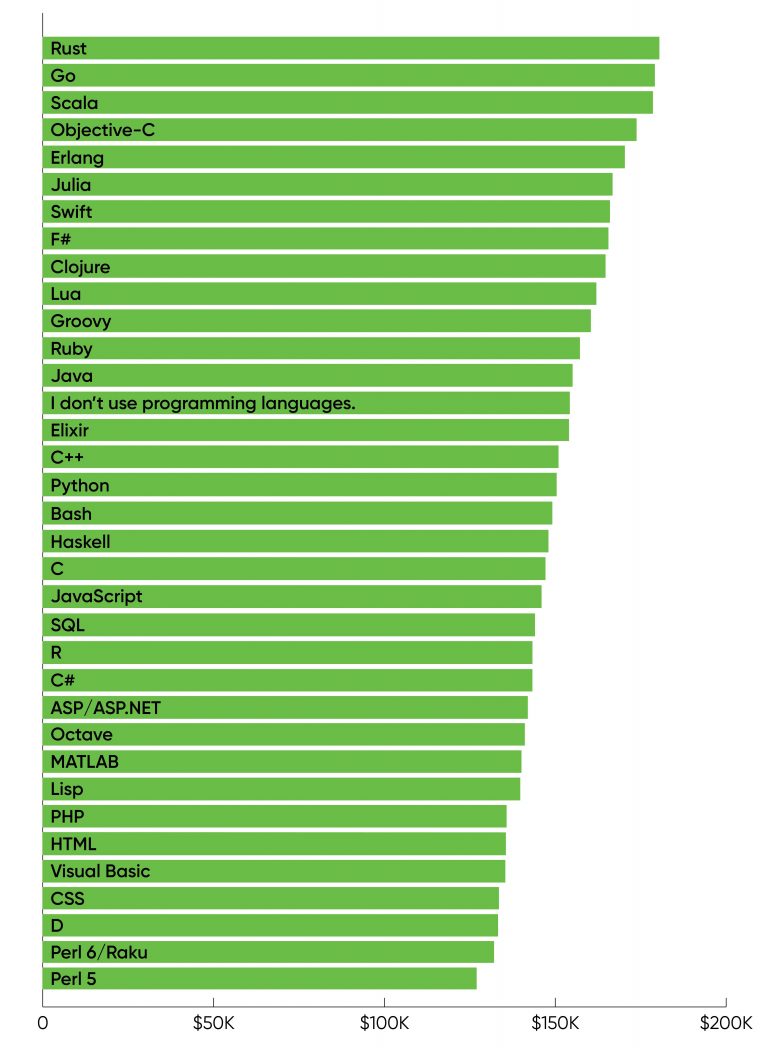
How will we clarify this? It’s tough to say that information and AI builders who use Rust command the next wage, since most respondents checked a number of languages. But we consider that this information reveals one thing important. The provide of expertise for newer languages like Rust and Go is comparatively small. While there is probably not an enormous demand for information scientists who use these languages (but), there’s clearly some demand—and with skilled Go and Rust programmers in brief provide, they command the next wage. Perhaps it’s even easier: whatever the language somebody will use at work, employers interpret data of Rust and Go as an indication of competence and willingness to be taught, which will increase candidates’ worth. An identical argument could be made for Scala, which is the native language for the extensively used Spark platform. Languages like Python and SQL are desk stakes: an applicant who can’t use them may simply be penalized, however competence doesn’t confer any particular distinction.
One shock is that 10% of the respondents stated that they didn’t use any programming languages. We’re unsure what which means. It’s attainable they labored totally in Excel, which needs to be thought-about a programming language however usually isn’t. It’s additionally attainable that they had been managers or executives who now not did any programming.
Salaries by Tool and Platform
We additionally requested respondents what instruments they used for statistics and machine studying and what platforms they used for information analytics and information administration. We noticed a number of the identical patterns that we noticed with programming languages. And the identical warning applies: respondents had been allowed to pick out a number of solutions to our questions in regards to the instruments and platforms that they use. (However, a number of solutions weren’t as frequent as for programming languages.) In addition, in the event you’re accustomed to instruments and platforms for machine studying and statistics, that the boundary between them is fuzzy. Is Spark a device or a platform? We thought-about it a platform, although two Spark libraries are within the checklist of instruments. What about Kafka? A platform, clearly, however a platform for constructing information pipelines that’s qualitatively totally different from a platform like Ray, Spark, or Hadoop.
Just as with programming languages, we discovered that probably the most extensively used instruments and platforms had been related to midrange salaries; older instruments, even when they’re nonetheless extensively used, had been related to decrease salaries; and a number of the instruments and platforms with the fewest customers corresponded to the very best salaries. (See Figure 5 for the complete checklist.)
The most typical responses to the query about instruments for machine studying or statistics had been “I don’t use any tools” (40%) or Excel (31%). Ignoring the query of how one does machine studying or statistics with out instruments, we’ll solely notice that those that didn’t use instruments had a mean wage of $143,000, and Excel customers had a mean wage of $138,000—each beneath common. Stata ($120,000) was additionally on the backside of the checklist; it’s an older bundle with comparatively few customers and is clearly falling out of favor.
The fashionable machine studying packages PyTorch (19% of customers, $166,000 common wage), TensorFlow (20%, $164,000), and scikit-learn (27%, $157,000) occupied the center floor. Those salaries had been above the common for all respondents, which was pulled down by the big numbers who didn’t use instruments or solely used Excel. The highest salaries had been related to H2O (3%, $183,000), KNIME (2%, $180,000), Spark NLP (5%, $179,000), and Spark MLlib (8%, $175,000). It’s onerous to belief conclusions primarily based on 2% or 3% of the respondents, however it seems that salaries are larger for individuals who work with instruments which have a variety of “buzz” however aren’t but extensively used. Employers pay a premium for specialised experience.
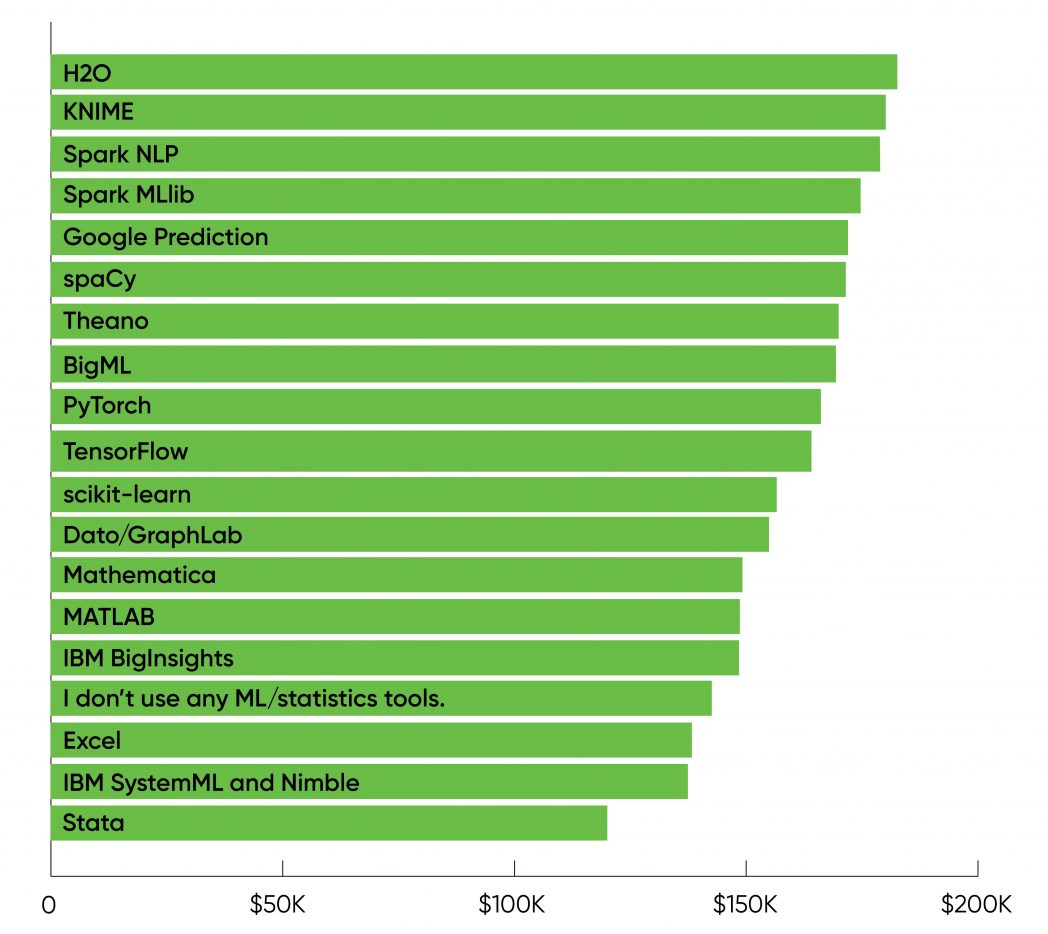
We see nearly precisely the identical factor after we take a look at information frameworks (Figure 6). Again, the commonest response was from individuals who didn’t use a framework; that group additionally obtained the bottom salaries (30% of customers, $133,000 common wage).
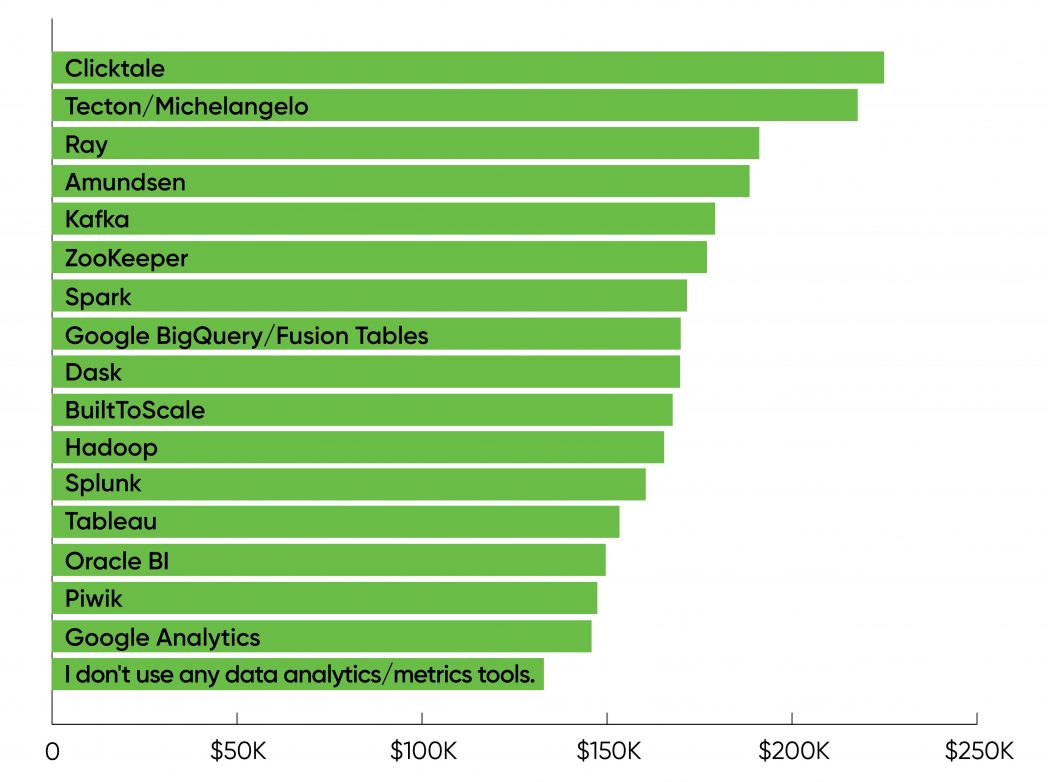
In 2021, Hadoop usually looks like legacy software program, however 15% of the respondents had been engaged on the Hadoop platform, with a mean wage of $166,000. That was above the common wage for all customers and on the low finish of the midrange for salaries sorted by platform.
The highest salaries had been related to Clicktale (now ContentSquare), a cloud-based analytics system for researching buyer expertise: solely 0.2% of respondents use it, however they’ve a mean wage of $225,000. Other frameworks related to excessive salaries had been Tecton (the business model of Michelangelo, at $218,000), Ray ($191,000), and Amundsen ($189,000). These frameworks had comparatively few customers—probably the most extensively used on this group was Amundsen with 0.8% of respondents (and once more, we warning in opposition to studying an excessive amount of into outcomes primarily based on so few respondents). All of those platforms are comparatively new, often mentioned within the tech press and social media, and look like rising healthily. Kafka, Spark, Google BigQuery, and Dask had been within the center, with a variety of customers (15%, 19%, 8%, and 5%) and above-average salaries ($179,000, $172,000, $170,000, and $170,000). Again, the preferred platforms occupied the center of the vary; expertise with much less often used and rising platforms commanded a premium.
Salaries by Industry
The best variety of respondents labored within the software program business (20% of the overall), adopted by consulting (11%) and healthcare, banking, and training (every at 8%). Relatively few respondents listed themselves as consultants (additionally 2%), although consultancy tends to be cyclic, relying on present considering on outsourcing, tax legislation, and different components. The common earnings for consultants was $150,000, which is just barely larger than the common for all respondents ($146,000). That might point out that we’re at the moment in some form of an equilibrium between consultants and in-house expertise.
While information evaluation has grow to be important to each form of enterprise and AI is discovering many purposes outdoors of computing, salaries had been highest within the pc business itself, as Figure 7 makes clear. For our functions, the “computer industry” was divided into 4 segments: pc {hardware}, cloud companies and internet hosting, safety, and software program. Average salaries in these industries ranged from $171,000 (for pc {hardware}) to $164,000 (for software program). Salaries for the promoting business (together with social media) had been surprisingly low, solely $150,000.
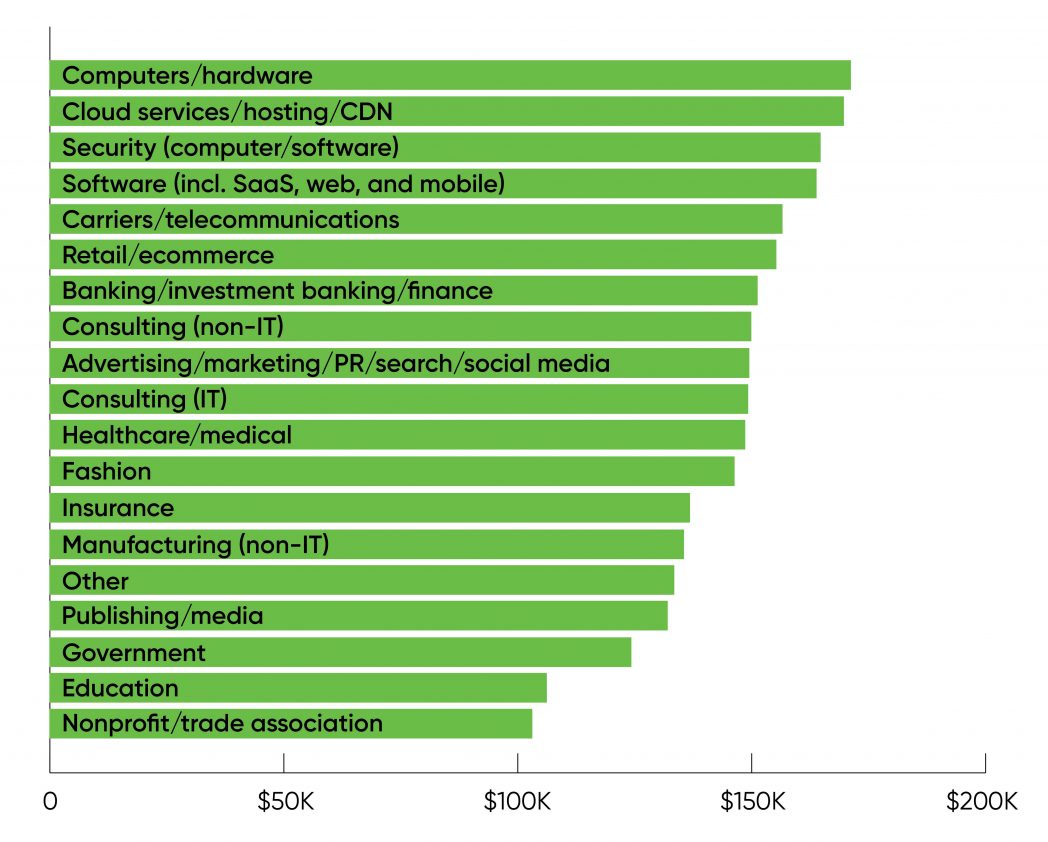
Education and nonprofit organizations (together with commerce associations) had been on the backside finish of the size, with compensation simply above $100,000 ($106,000 and $103,000, respectively). Salaries for technical employees in authorities had been barely larger ($124,000).
Salaries by State
When taking a look at information and AI practitioners geographically, there weren’t any large surprises. The states with probably the most respondents had been California, New York, Texas, and Massachusetts. California accounted for 19% of the overall, with over double the variety of respondents from New York (8%). To perceive how these 4 states dominate, keep in mind that they make up 42% of our respondents however solely 27% of the United States’ inhabitants.
Salaries in California had been the very best, averaging $176,000. The Eastern Seaboard did effectively, with a mean wage of $157,000 in Massachusetts (second highest). New York, Delaware, New Jersey, Maryland, and Washington, DC, all reported common salaries within the neighborhood of $150,000 (as did North Dakota, with 5 respondents). The common wage reported for Texas was $148,000, which is barely above the nationwide common however however appears on the low facet for a state with a major know-how business.
Salaries within the Pacific Northwest weren’t as excessive as we anticipated. Washington simply barely made it into the highest 10 when it comes to the variety of respondents, and common salaries in Washington and Oregon had been $138,000 and $133,000, respectively. (See Figure 8 for the complete checklist.)
The highest-paying jobs, with salaries over $300,000, had been concentrated in California (5% of the state’s respondents) and Massachusetts (4%). There had been a couple of attention-grabbing outliers: North Dakota and Nevada each had only a few respondents, however every had one respondent making over $300,000. In Nevada, we’re guessing that’s somebody who works for the on line casino business—in spite of everything, the origins of chance and statistics are tied to playing. Most states had no respondents with compensation over $300,000.
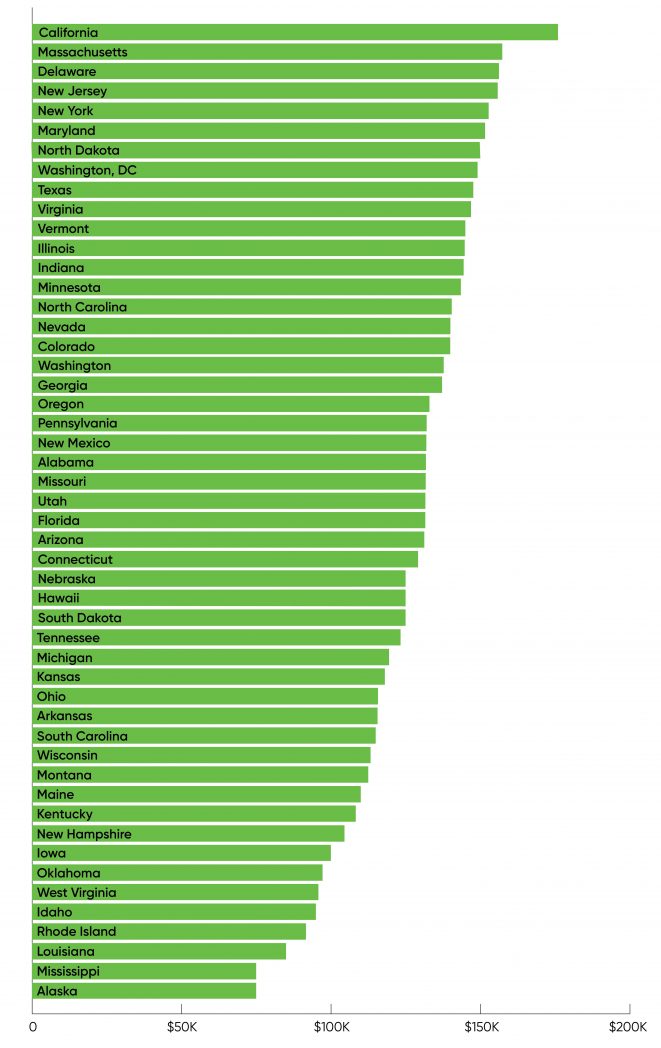
The lowest salaries had been, for probably the most half, from states with the fewest respondents. We’re reluctant to say greater than that. These states sometimes had beneath 10 respondents, which implies that averaging salaries is extraordinarily noisy. For instance, Alaska solely had two respondents and a mean wage of $75,000; Mississippi and Louisiana every solely had 5 respondents, and Rhode Island solely had three. In any of those states, one or two further respondents on the government degree would have an enormous impact on the states common. Furthermore, the averages in these states are so low that each one (or nearly all) respondents have to be college students, interns, or in entry-level positions. So we don’t suppose we are able to make any assertion stronger than “the high paying jobs are where you’d expect them to be.”
Job Change by Salary
Despite the variations between states, we discovered that the will to alter jobs primarily based on lack of compensation didn’t rely considerably on geography. There had been outliers at each extremes, however they had been all in states the place the variety of respondents was small and one or two folks trying to change jobs would make a major distinction. It’s not terribly attention-grabbing to say that 24% of respondents from California intend to alter jobs (solely 2% above the nationwide common); in spite of everything, you’d anticipate California to dominate. There could also be a small sign from states like New York, with 232 respondents, of whom 27% intend to alter jobs, or from a state like Virginia, with 137 respondents, of whom solely 19% had been considering of fixing. But once more, these numbers aren’t a lot totally different from the overall share of attainable job changers.
If intent to alter jobs because of compensation isn’t depending on location, then what does it rely on? Salary. It’s under no circumstances shocking that respondents with the bottom salaries (beneath $50,000/yr) are extremely motivated to alter jobs (29%); this group consists largely of scholars, interns, and others who’re beginning their careers. The group that confirmed the second highest want to alter jobs, nevertheless, had the very best salaries: over $400,000/yr (27%). It’s an attention-grabbing pairing: these with the very best and lowest salaries had been most intent on getting a wage enhance.
26% of these with annual salaries between $50,000 and $100,000 indicated that they intend to alter jobs due to compensation. For the rest of the respondents (these with salaries between $100,000 and $400,000), the share who intend to alter jobs was 22% or decrease.
Salaries by Certification
Over a 3rd of the respondents (37%) replied that they hadn’t obtained any certifications up to now yr. The subsequent greatest group replied “other” (14%), that means that they’d obtained certifications up to now yr however not one of many certifications we listed. We allowed them to put in writing in their very own responses, and so they shared 352 distinctive solutions, starting from vendor-specific certifications (e.g., DataRobotic) to school levels (e.g., University of Texas) to well-established certifications in any variety of fields (e.g., Certified Information Systems Security Professional a.okay.a. CISSP). While there have been definitely instances the place respondents used totally different phrases to explain the identical factor, the quantity of distinctive write-in responses displays the good variety of certifications obtainable.
Cloud certifications had been by far the preferred. The prime certification was for AWS (3.9% obtained AWS Certified Solutions Architect-Associate), adopted by Microsoft Azure (3.8% had AZ-900: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals), then two extra AWS certifications and CompTIA’s Security+ certification (1% every). Keep in thoughts that 1% solely represents 27 respondents, and all the opposite certifications had even fewer respondents.
As Figure 9 reveals, the very best salaries had been related to AWS certifications, the Microsoft AZ-104 (Azure Administrator Associate) certification, and the CISSP safety certification. The common wage for folks itemizing these certifications was larger than the common wage for US respondents as a complete. And the common wage for respondents who wrote in a certification was barely above the common for individuals who didn’t earn any certifications ($149,000 versus $143,000).
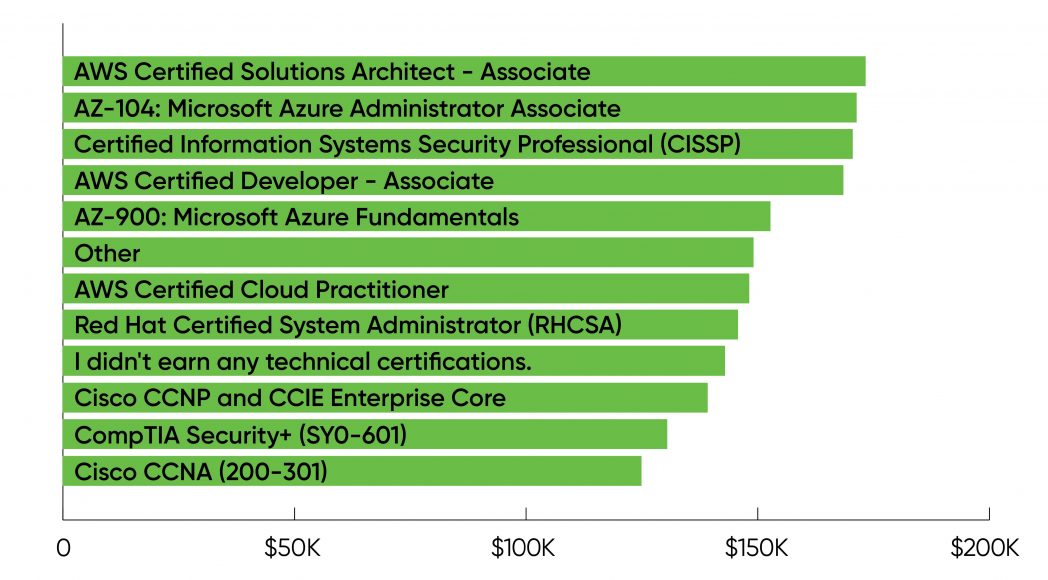
Certifications had been additionally related to wage will increase (Figure 10). Again AWS and Microsoft Azure dominate, with Microsoft’s AZ-104 main the way in which, adopted by three AWS certifications. And on the entire, respondents with certifications seem to have obtained bigger wage will increase than those that didn’t earn any technical certifications.
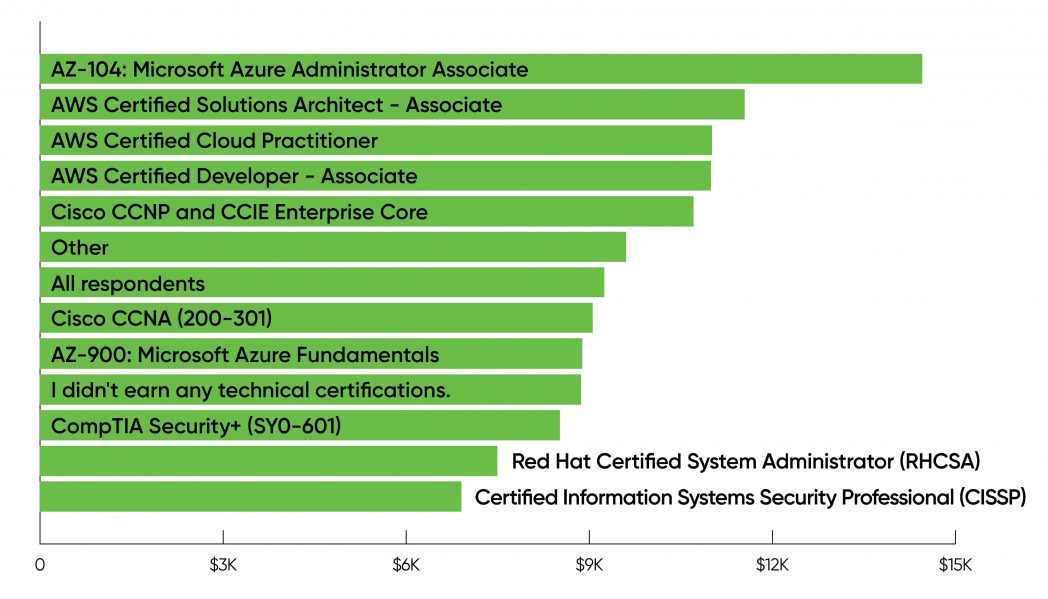
Google Cloud is an apparent omission from this story. While Google is the third-most-important cloud supplier, solely 26 respondents (roughly 1%) claimed any Google certification, all beneath the “Other” class.
Among our respondents, safety certifications had been comparatively unusual and didn’t look like related to considerably larger salaries or wage will increase. Cisco’s CCNP was related to larger wage will increase; respondents who earned the CompTIA Security+ or CISSP certifications obtained smaller will increase. Does this replicate that administration undervalues safety coaching? If this speculation is right, undervaluing safety is clearly a major mistake, given the continued significance of safety and the potential for new assaults in opposition to AI and different data-driven techniques.
Cloud certifications clearly had the best impact on wage will increase. With only a few exceptions, any certification was higher than no certification: respondents who wrote in a certification beneath “Other” averaged a $9,600 wage enhance over the previous couple of years, versus $8,900 for respondents who didn’t get hold of a certification and $9,300 for all respondents no matter certification.
Training
Participating in coaching resulted in wage will increase—however solely for individuals who spent greater than 100 hours in a coaching program. As Figure 11 reveals, these respondents had a mean wage enhance of $11,000. This was additionally the biggest group of respondents (19%). Respondents who solely reported endeavor 1–19 hours of coaching (8%) noticed decrease wage will increase, with a mean of $7,100. It’s attention-grabbing that those that participated in 1–19 hours of coaching noticed smaller will increase than those that didn’t take part in coaching in any respect. It doesn’t make sense to invest about this distinction, however the information does make one factor clear: in the event you have interaction in coaching, be critical about it.
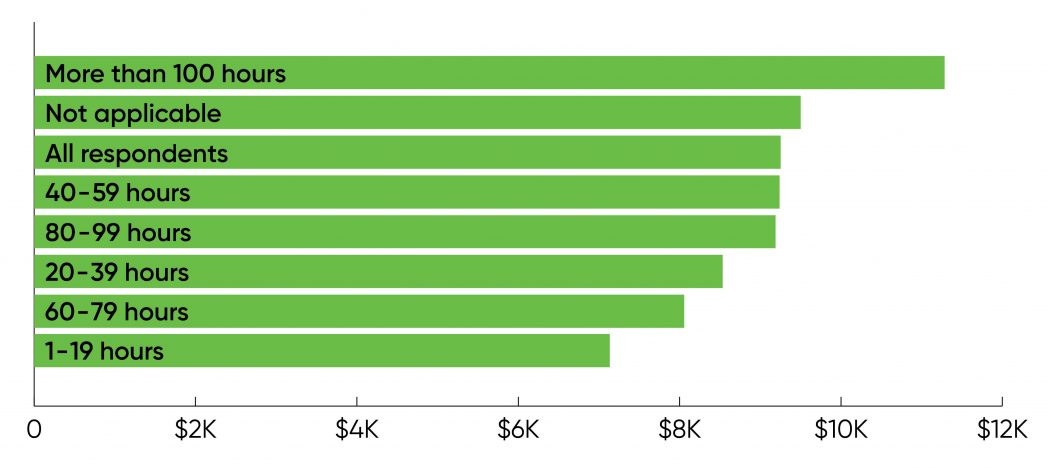
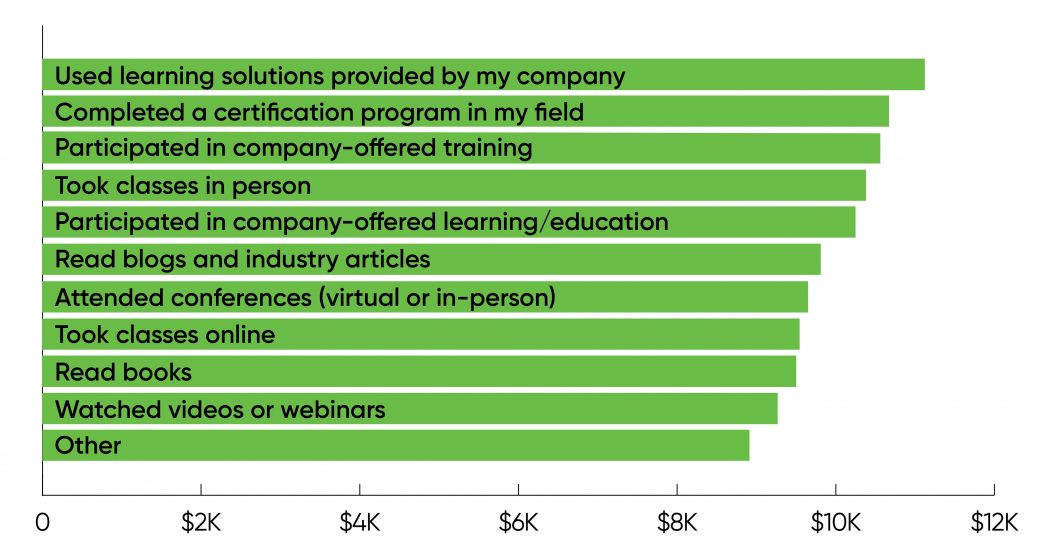
We additionally requested what varieties of coaching respondents engaged in: whether or not it was firm offered (for which there have been three options), a certification program, a convention, or another form of coaching (detailed in Figure 12). Respondents who took benefit of company-provided alternatives had the very best common salaries ($156,000, $150,000, and $149,000). Those who obtained certifications had been subsequent ($148,000). The outcomes are related if we take a look at wage will increase over the previous three years: Those who participated in varied types of company-offered coaching obtained will increase between $11,000 and $10,000. Salary will increase for respondents who obtained a certification had been in the identical vary ($11,000).
The Last Word
Data and AI professionals—a rubric beneath which we embrace information scientists, information engineers, and specialists in AI and ML—are well-paid, reporting a mean wage slightly below $150,000. However, there have been sharp state-by-state variations: salaries had been considerably larger in California, although the Northeast (with some exceptions) did effectively.
There had been additionally important variations between salaries for women and men. Men’s salaries had been larger no matter job title, no matter coaching and no matter tutorial levels—though girls had been extra more likely to have a sophisticated tutorial diploma (PhD or grasp’s diploma) than had been males.
We don’t see proof of a “great resignation.” Job turnover by way of the pandemic was roughly what we’d anticipate (maybe barely beneath regular). Respondents did look like involved about job safety, although they didn’t need to admit it explicitly. But except for the least- and most-highly compensated respondents, the intent to alter jobs due to wage was surprisingly constant and nothing to be alarmed at.
Training was necessary, partially as a result of it was related to hireability and job safety however extra as a result of respondents had been genuinely occupied with studying new expertise and bettering present ones. Cloud coaching, notably in AWS and Microsoft Azure, was probably the most strongly related to larger wage will increase.
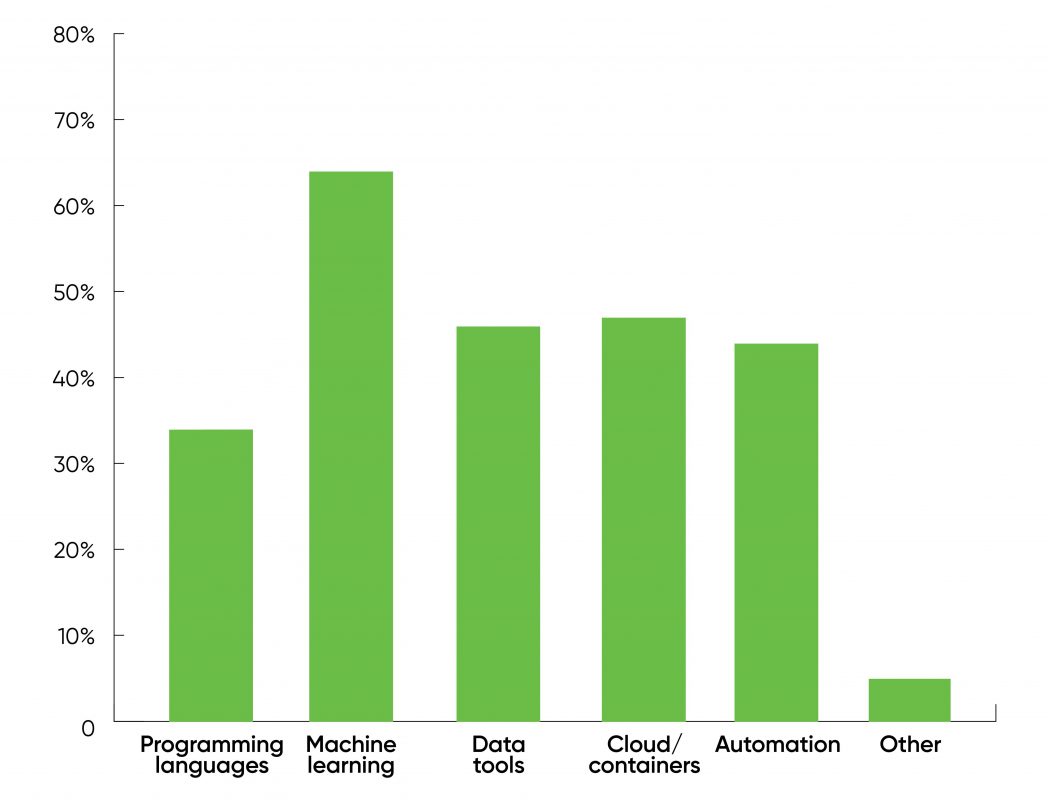
But maybe we should always go away the final phrase to our respondents. The remaining query in our survey requested what areas of know-how would have the most important impact on wage and promotions within the coming yr. It wasn’t a shock that many of the respondents stated machine studying (63%)—today, ML is the most popular matter within the information world. It was extra of a shock that “programming languages” was famous by simply 34% of respondents. (Only “Other” obtained fewer responses—see Figure 13 for full particulars.) Our respondents clearly aren’t impressed by programming languages, though the information means that employers are prepared to pay a premium for Rust, Go, and Scala.
There’s one other sign price taking note of if we glance past the extremes. Data instruments, cloud and containers, and automation had been almost tied (46, 47, and 44%). The cloud and containers class contains instruments like Docker and Kubernetes, cloud suppliers like AWS and Microsoft Azure, and disciplines like MLOps. The instruments class contains instruments for constructing and sustaining information pipelines, like Kafka. “Automation” can imply a variety of issues however on this context most likely means automated coaching and deployment.
We’ve argued for a while that operations—efficiently deploying and managing purposes in manufacturing—is the most important problem going through ML practitioners within the coming years. If you need to keep on prime of what’s taking place in information, and if you wish to maximize your job safety, hireability, and wage, don’t simply discover ways to construct AI fashions; discover ways to deploy purposes that stay within the cloud.
In the traditional film The Graduate, one character famously says, “There’s a great future in plastics. Think about it.” In 2021, and with out being anyplace close to as repulsive, we’d say, “There’s a great future in the cloud. Think about it.”
[ad_2]

