[ad_1]
That is the conclusion from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services National Health Expenditure Projections. The paper–revealed in Health Affairs—summarizes the spending modifications as follows:
National well being expenditures are projected to develop 5.4 p.c, on common, over the course of 2022–31 and to account for roughly 20 p.c of the financial system by the tip of that interval. The insured share of the inhabitants is anticipated to exceed 92 p.c by means of 2023, partially on account of record-high Medicaid enrollment, after which decline towards 90 p.c as protection necessities associated to the COVID-19 public well being emergency expire. The prescription drug provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 are anticipated to decrease out-of-pocket spending for Medicare Part D enrollees starting in 2024 and to end in financial savings to Medicare starting in 2031.
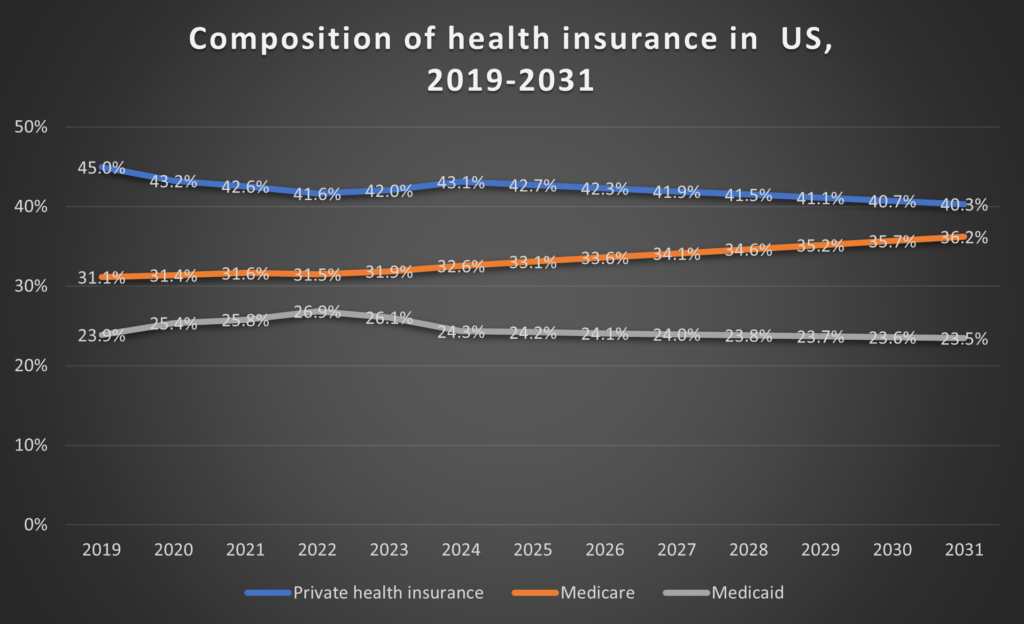
As the inhabitants ages, we see that Medicare will make up a rising share of the insured people within the US. Note that the determine beneath solely contains Medicare, Medicaid and Private insurance coverage and linearly interpolates these charges between 2024 and 2031.
Regarding the impression of the Inflation Reduction Act, the authors write:
One provision from the Inflation Reduction Act that’s anticipated to place upward strain on Medicare spending development is the anticipated outlays that this system pays to cowl the cap on Part D out-of-pocket spending at $2,000 per yr, which takes impact in 2025. However, Medicare is predicted to expertise slower development in spending towards the ultimate years of the projection interval, reflecting the total impact of the Inflation Reduction Act’s provisions that enable this system to barter costs for sure Part D medicine and that hyperlink drug value will increase to the CPI.
The full article is obtainable right here.
